Figure 2.
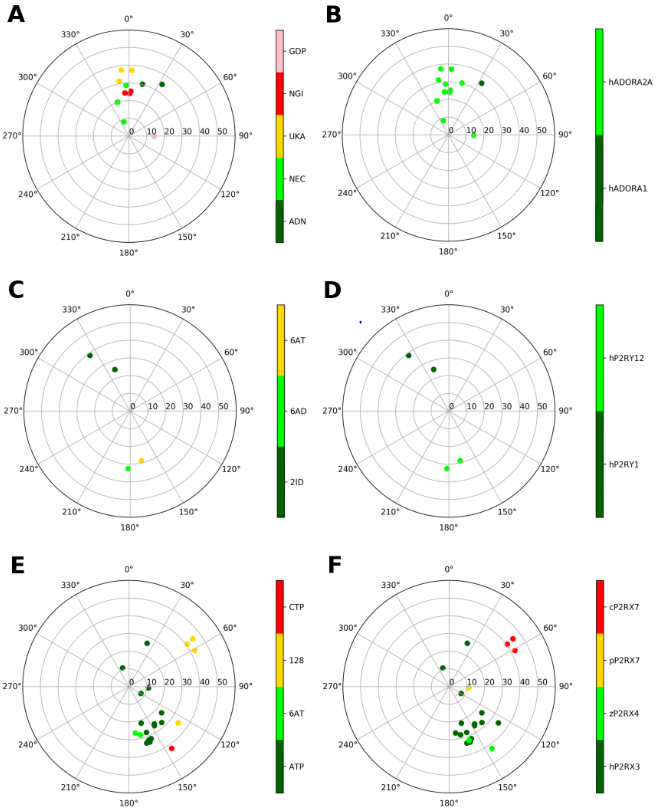
Representation of the ribose conformations of purinergic receptors, shown on the pseudorotational cycle (P on polar axes, νmax on x and y axes). The plots on the left and on the right depict the data on a per-ligand (residue name according to PDB file) and per-protein (species and gene name) basis. A and B. A1 and A2AARs (all human). Nucleoside ligands in (A) are labeled as: ADN (adenosine), NEC (NECA), UKA (UK432097), NGI (CGS21680). GDP is also present in one of the structures (5G53), where it is bound to a Gs protein. C and D. P2Y1 and P2Y12Rs (all human). Nucleotide ligands in (C) are labeled according as: 2ID (MRS2500), 6AD (2MeSADP), 6AT (2MeSATP). E and F. Ribose conformations at P2XRs (all species, as indicated) are shown for human P2RX3, Danio rerio (zebrafish) P2RX4, Ailuropoda melanoleuca (giant panda) P2RX7, Gallus gallus (chicken) P2RX7; with ligands: ATP, 6AT (2MeSATP), 128 (TNP-ATP (spiro-trinitrobenzene-ATP)), CTP.
