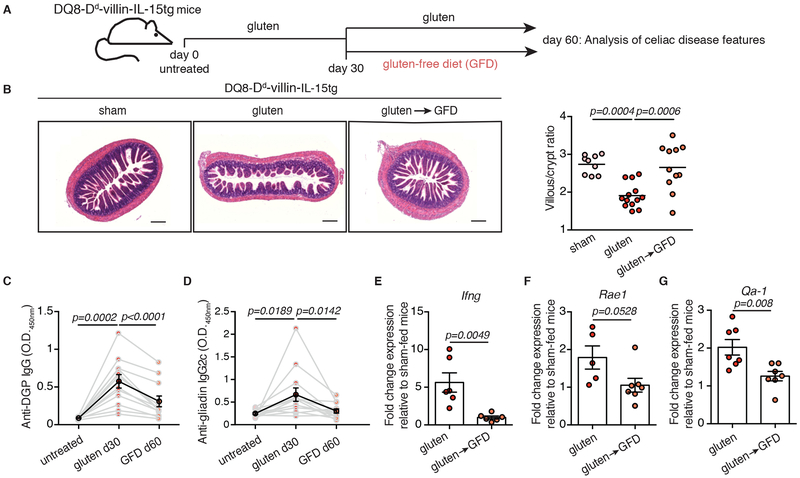
Figure 1. DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice: a gluten-dependent model of CeD with villous atrophy.
(A-G) DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice were maintained on a GFD (sham), fed with gluten for 60 days (gluten), or fed with gluten for 30 days and then reverted to a GFD (gluten→GFD) for 30 days.
(A) Experimental timeline.
(B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of paraffin-embedded ileum sections. Scale bar, 200 μm. The graph depicts the ratio of the morphometric assessment of villous height to crypt depth. (sham, n=9; gluten, n=13; gluten→GFD, n=11 mice, four independent experiments). ANOVA) / Tukey’s multiple comparison; mean.
(C) Serum anti-deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) IgG levels were measured by ELISA. Sera were collected sequentially from four independent experiments in the same mice (n=12) before gluten feeding (untreated), thirty days after gluten feeding (gluten d30), and thirty days after reversion to a GFD (GFD d60). The black line represents the average mean ± s.e.m.. Paired, two-tailed, t-test.
(D) Serum anti-gliadin IgG2c levels measured as in (C) (n=12 mice per group, four independent experiments). Paired, two-tailed, t-test.
(E) Expression of IFN-γ in the LP was measured by qPCR. Relative expression levels in gluten-fed (n=6) and gluten→GFD (n=6) mice were normalized against the expression levels observed in sham-fed DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice. Two independent experiments; Unpaired, two-tailed, t-test.
(F, G) Expression of Rae1 (gluten, n=5; gluten→GFD, n=7) (F) and Qa-1 (gluten, n=7; gluten→GFD, n=7) (G) in the intestinal epithelium measured by qPCR as in (E). Two independent experiments; mean ± s.e.m; Unpaired, two-tailed, t-test.