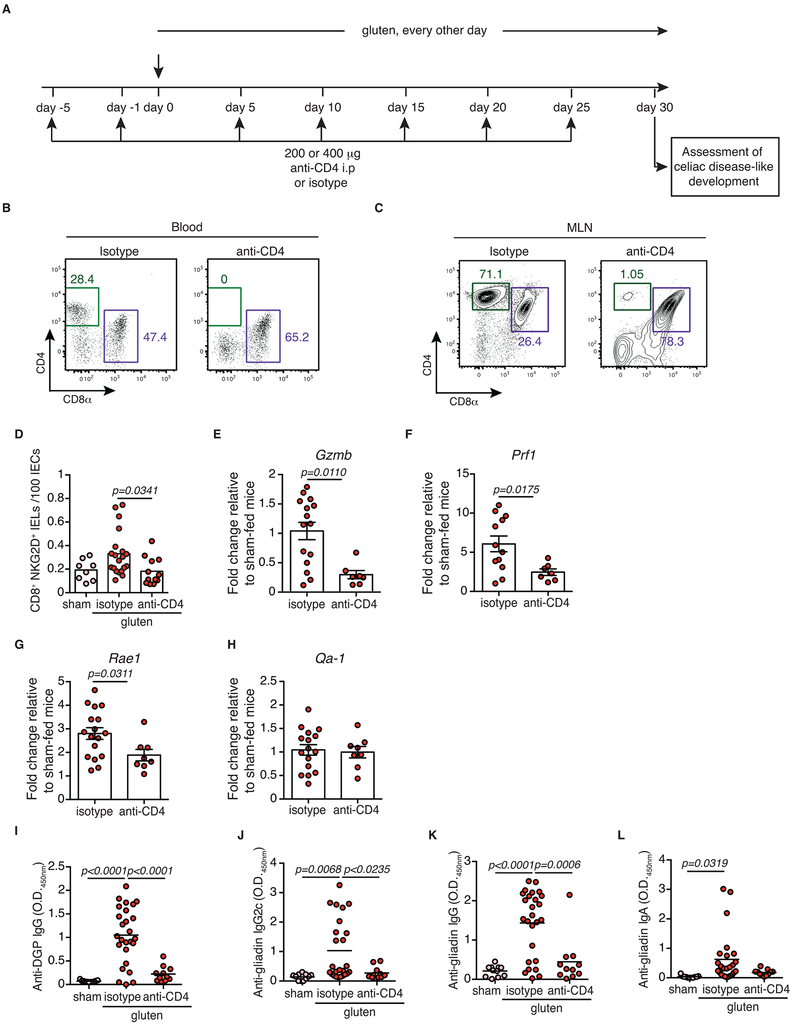
Extended Data Figure 7. CD4+ T cells are required for coeliac disease pathogenesis.
(A-J) DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice were treated with 200 or 400 μg of depleting anti-CD4 antibody (clone GK1.5) or its isotype control (rat IgG2b) twice prior to and during the course of gluten feeding.
(A) Experimental scheme.
(B, C) Representative dot-plots showing depletion efficiency in the (B) blood and (C) mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) of DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice.
(D) The intestinal epithelium was isolated and analyzed by flow cytometry. IELs were identified as TCRβ+ CD4− CD8+ cells. NKG2D+ NKG2− IELs are indicated by absolute number / 100 IECs. Four independent experiments (sham, n=8; gluten + isotype, n=20, gluten + anti-CD4, n=12); mean; ANOVA / Tukey’s multiple comparison.
(E-H) Expression of (E) GzmB, (F) Prf1, (G) Rae1, and (H) Qa-1 in the intestinal epithelium as measured by qPCR. Relative expression levels were normalized against the expression levels observed in sham-fed DQ8-Dd-villin-IL-15tg mice. Four independent experiments ± s.e.m (gluten + isotype, n=12 to 17, gluten + anti-CD4, n=8); mean; Unpaired, two-tailed, t-test.
(I, L) Anti-DGP IgG (I), anti-gliadin IgG2c (J), anti-gliadin IgG (K) and anti-gliadin IgA (L) levels were measured by ELISA from serum collected thirty days after gluten feeding. Four independent experiments (sham, n=11; gluten + isotype, n=25-26, gluten + anti-CD4, n=11); mean; ANOVA / Tukey’s multiple comparison.