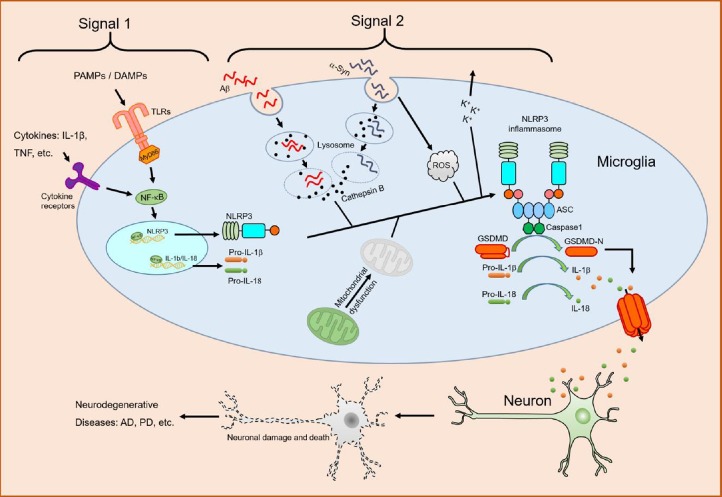
Figure 1.
Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases.
Cytokines, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) engage their receptors, leading to activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and subsequent upregulation of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 protein (NLRP3) and pro-IL-1β (Signal 1). Phagocytosis of misfolded amyloid-β (Aβ) or α-synuclein (α-Syn) induces lysosomal damage and subsequent release of cathepsin B and ROS accumulation, which trigger NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and caspase1 activation (Signal 2). Activated caspase1 cleaves pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18 and gasdermin D (GSDMD) into their bioactive forms. Mitochondrial dysfunction, K+ efflux, or both might also contribute to NLRP3 inflammasome activation by Aβ or α-Syn. Proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-18, or other inflammatory mediators induce neuronal damage and death, leading to neurodegenerative diseases. AD: Alzheimer’s disease; IL: interleukin; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 protein; PD: Parkinson’s disease; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TLR: Toll-like receptor.