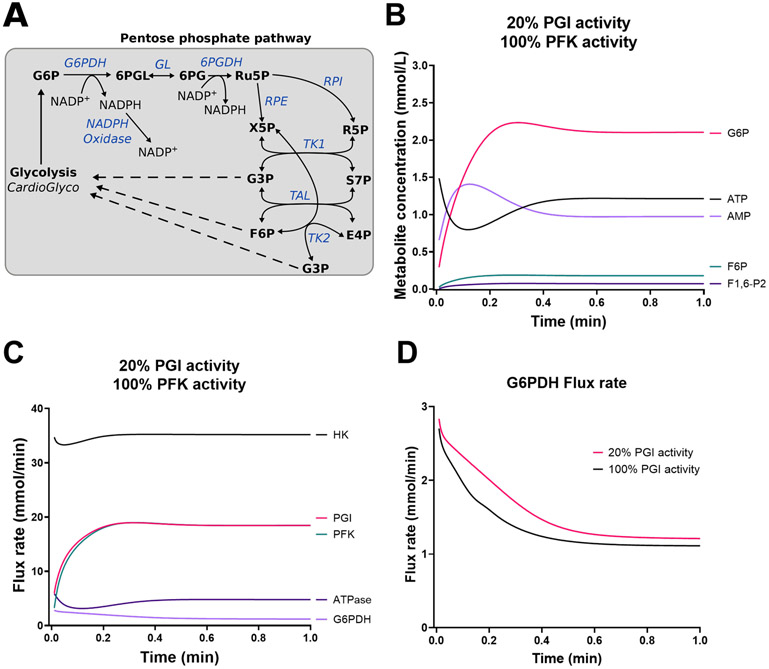
Figure 6. Kinetic modeling of phosphoglucose isomerase inhibition reveals redirection of glycolytic intermediates into the pentose phosphate pathway.
(A) Pentose phosphate pathway expansion of CardioGlyco. (B-C) Predicted metabolite concentrations (B) and flux rates (C) in response to PGI inhibition (20% activity). PFK activity was not changed. Extracellular glucose supply was set to 5.5 mmol/L during the simulations. (D) Comparison of G6PDH flux rate at 20% and 100% PGI activity. Simulations indicated that PGI inhibition promotes G6P accumulation and an increased G6PDH flux rate.