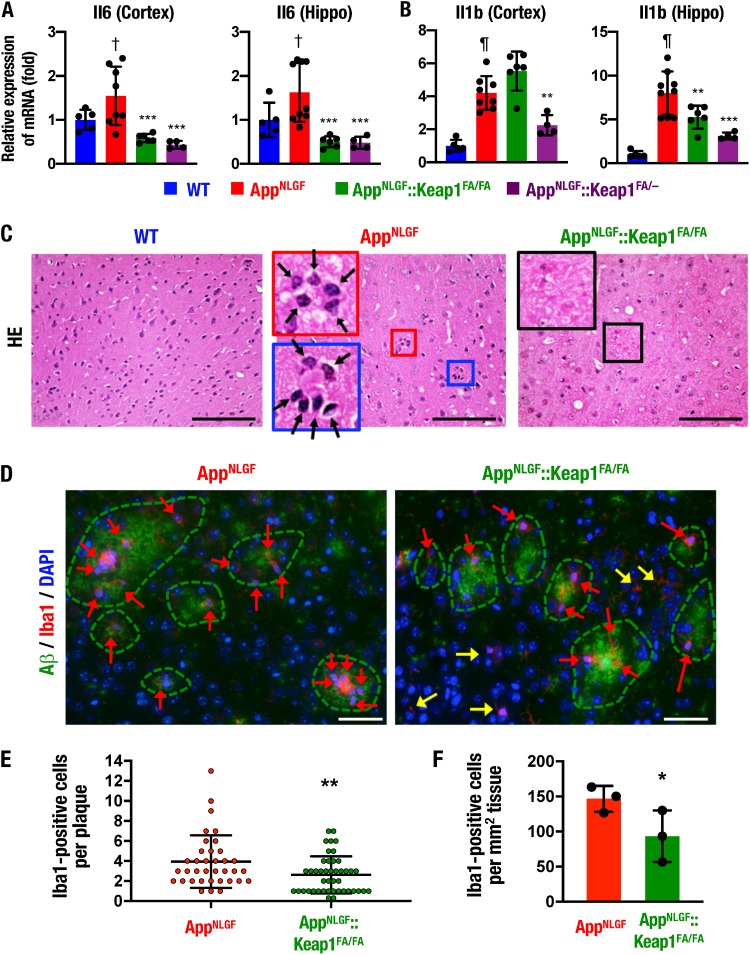
FIG 3.
Proinflammatory response and phagocytic cells and Nrf2 expression in the AppNLGF mouse brain. (A and B) Expression levels of Il6 (A) and Il1b (B) gene mRNAs in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus (Hippo), normalized by Actb gene expression. The expression levels of WT mice were set to 1. (C) HE staining in the cerebral cortices of WT, AppNLGF, and AppNLGF::Keap1FA/FA mice. Arrows, phagocytic cells. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of Aβ (green) and Iba1 (red) in the AppNLGF and AppNLGF::Keap1FA/FA mouse cortex. Red and yellow arrows indicate plaque-related and plaque-unrelated Iba1-positive cells, respectively. (E) Numbers of Iba1-positive cells in each amyloid plaque in the cerebral cortex. Thirty-six plaques from three AppNLGF mouse cortices and 44 plaques from three AppNLGF::Keap1FA/FA mouse cortices were counted. (F) Numbers of Iba1-positive cells associated with amyloid plaque per tissue area (square millimeter) in the cerebral cortex. The averages of the numbers in each mouse were calculated in three AppNLGF and three AppNLGF::Keap1FA/FA mice. The results are presented as means ± the SD. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA, followed by Fisher LSD post hoc test (A and B) or Student t test (E and F). †, P < 0.05; ¶, P < 0.001 versus WT mice. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 versus AppNLGF mice. Scale bars: 100 μm (C) and 50 μm (D).