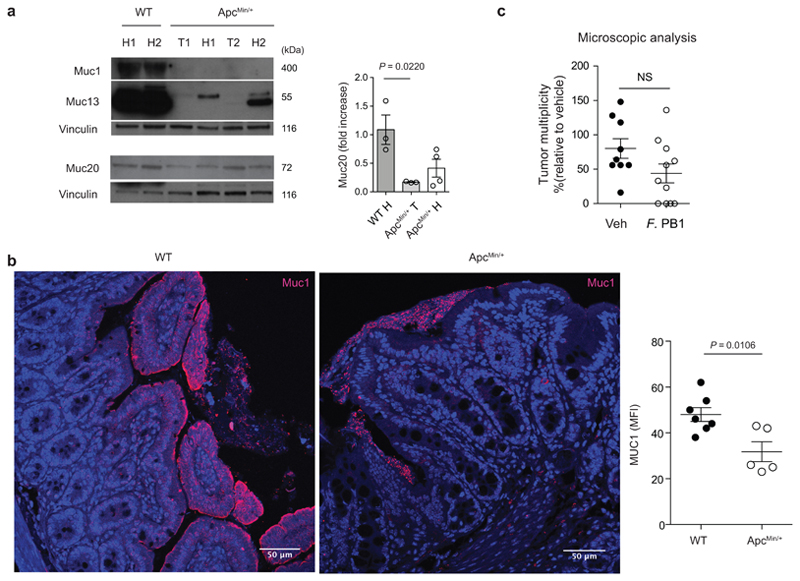
Extended Data Fig. 2. Mucin production is altered in the ileum of ApcMin/+ mice.
a, Representative Western blots of two independent experiments with consistent results showing the abundance of Muc1, Muc13 and Muc20 in ileal extracts from WT (healthy tissues, H) and healthy (H) and tumor (T) tissues of ApcMin/+ mice analyzed at 11 weeks of age; Right: densitometric quantification (WT n = 3; ApcMin/+ n = 4 biologically independent samples). b, Representative confocal images of WT and ApcMin/+ mice ileum intestinal tissues stained with Muc1 (red) and DAPI (blue); scale bars, 50 μm. Mean fluorescence intensity of MUC1 was measured to quantify the expression of the protein in the intestinal of ApcMin/+ and WT mice (WT n = 7, ApcMin/+ n = 5 biologically independent samples). c, ApcMin/+ mice were treated with vehicle (n = 10 mice/group) or F. PB1 (n = 11 mice/group) from week 8 to 10. Number of microscopic lesions, shown as % relative to vehicle, was evaluated on H&E slides by an expert pathologist. a-c, Data from two independent experiments and represented as means ± s.e.m.. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA using Tukey post-test (a), two tailed unpaired Mann Whitney test (b), or two-tailed unpaired t-test (c).