Figure 7.
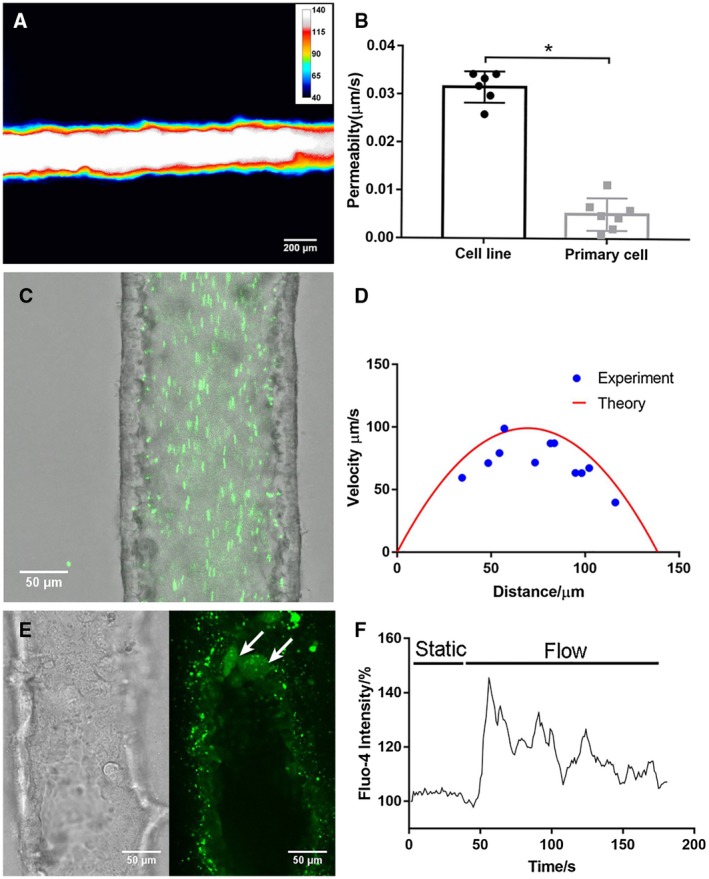
A bile duct‐on‐a‐chip constructed with primary extrahepatic cholangiocytes demonstrated better barrier function than the cell line. (A) Representative pseudo color image of FITC‐dextran (4 kDa) in a channel, imaged after 10 minutes (n = 7). Scale bars, 200 μm. (B) Permeability of the cholangiocyte cell line and primary extrahepatic cholangiocyte‐lined channel to 4‐kDa FITC‐dextran, n ≥ 6 devices. (C) Fluorescent microbeads (green, 0.2 μm) flowing through the cholangiocyte channel (cell line) at 0.02 dyne/cm2. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Theoretical and experimental velocity profile of luminal fluid flow in the cholangiocyte channel at 0.02 dyne/cm2. (E) Bright‐field image and fluorescent image of activated primary cholangiocytes (white arrow) visualized with Fluo‐4 fluorescence in the channel under shear flow. (F) Representative tracing of intracellular Fluo‐4 fluorescence in response to luminal flow at 3.9 dyne/cm2. All data are presented as mean ± SD; *P < 0.05.
