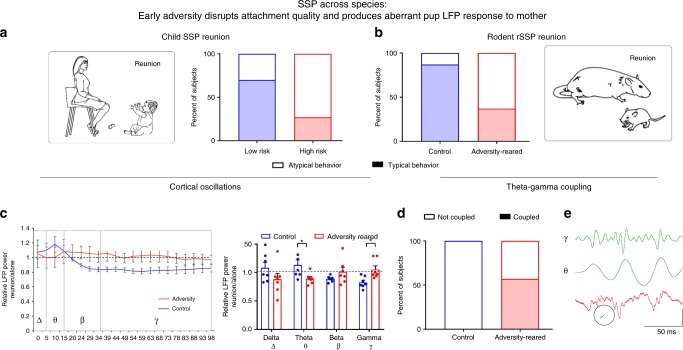
Fig. 3. Across species, compromised early care disrupts attachment uncovered by separation and reunion with the caregiver in the SSP.
a In children, biographical factors (e.g., SES and housing stability) generated classifications of risk. During the SSP, prosocial behaviors were observed more often in low-risk children, while atypical reunion behaviors were more frequently observed in high-risk children. b Adversity-reared rat pups showed atypical responses to the caregiver during the SSP reunion epoch. Across species, atypical reunion behaviors observed in the child SSP and rodent rSSP included contradictory responses to the parent or misdirected behaviors. c In rat pups, reunion with the mother decreased high frequency oscillations in the control-reared pups (normalized to power during epoch 5: pup alone, data from 5 control and 5 adversity-reared litters). This decrease was not observed in adversity-reared pups; unlike controls, theta power was decreased. Bars represent mean ± standard error (SEM) of power collapsed into frequency bands. Dashed line = no change from pup alone. Frequency bands labeled are delta (δ), theta (θ), beta (β), and gamma (γ). d In rat pups, theta-gamma coupling was observed more reliably in adversity-reared pups than control-reared pups. e Rat pup example of raw voltage trace (red) and gamma (γ)/theta (θ) filters (green); scale bar: vertical is 10 µV in theta/gamma, 25 µV in raw trace. Circle shows phase locking vector length = 0.0581, −122.36°. *p < 0.05, ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.