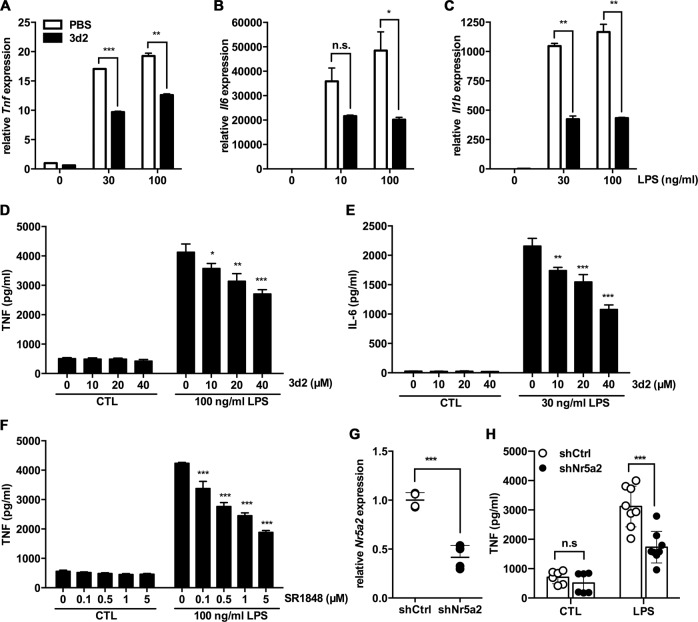
Fig. 2. LRH-1 inhibition reduces the pro-inflammatory cytokine production in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.
mRNA expression levels of a Tnf, b Il6, and c Il1b in RAW 264.7 cells pre-treated for 2 h with vehicle (PBS) or 3d2 (40 μM) and subsequently stimulated with control buffer (CTL) or LPS at indicated concentrations for 18 h. Results are shown as relative to murine Gapdh mRNA expression. Mean values of triplicates ± SD of three independent experiments are shown (t test; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). d TNF and e IL-6 secreted levels in the supernatant of RAW 264.7 cells pre-treated with indicated concentrations of 3d2 for 2 h and subsequently stimulated with control buffer (CTL) or LPS at indicated concentrations for 18 h. f TNF secreted levels in the supernatant of RAW 264.7 cells pre-treated for 2 h with SR1848 at indicated concentrations, prior to stimulation with control buffer (CTL) or LPS at indicated concentrations for 18 h. Mean values of triplicates ± SD of a representative experiment (n = 3) are shown (one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). g Quantification of mRNA levels of Nr5a2 in RAW 264.7 cells transduced with shRNA against Nr5a2 (shNr5a2) or shRNA control (shCtrl). Data are shown as relative to murine Actb mRNA and expressed as fold change to shCtrl cells. h TNF produced in RAW 264.7 cells transduced with shNr5a2 or shCtrl control and subsequent treated with control buffer (CTL) or LPS (30 ng/mL) for 18 h. Dots show technical replicates and bars means ± SD of data pooled from two independent experiment (two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s., not significant).