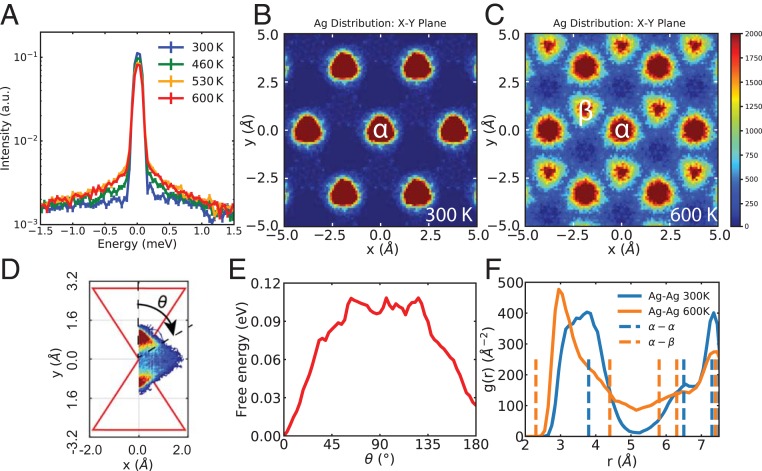
Fig. 5.
Superionic diffusion of Ag ions and the diffusion barrier. () Quasielastic neutron scattering from CNCS with 4 meV at 300, 460, 530, and 600 K, respectively, integrated over 1.4 1.6. The Lorentzian width increasing on heating represents faster diffusion. (B and C) In-plane probability distribution of Ag atoms from AIMD at () 300 K and () 600 K. At 300 K, Ag atoms vibrate near their equilibrium positions at sites. The diffusion occurs occasionally at 300 K and becomes dominant at 600 K. Threefold rotation symmetry and periodicity are applied to the plot. () The probability density of Ag atoms on the plane perpendicular to the shared edge of neighboring and sites. The upper red triangle is the projection of the -tetrahedron, and the lower one is the -tetrahedron. The angle between the Ag atom positions and the center of the -tetrahedron is defined as the reaction coordinate. () The free-energy barrier along the reaction pathway. A low barrier of 0.11 eV is observed along an extended region between and sites. () Pair distribution function projected on Ag–Ag bonds at 300 K (blue) and 600 K (orange). Dashed lines are the distances between – and the – sites. Strong repulsion between Ag atoms is observed, as no Ag–Ag bond with length of 2.3 Å (the nearest – distance) appears in AIMD.