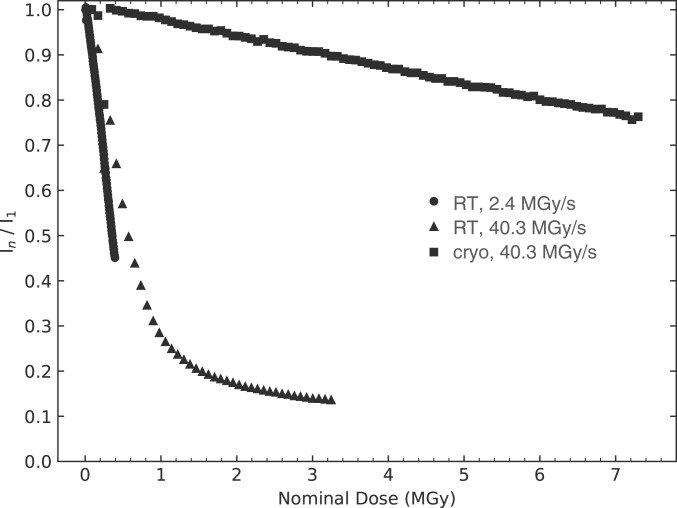
Fig. 2.
Decrease in diffraction power as a function of increasing average dose. The sum of the intensities of all reflections up to the detector edges in all indexed diffraction patterns of a dataset, normalized by the sum of the first (i.e., lowest dose) dataset are shown as a function of the average dose delivered by a Gaussian beam (ADG95, average over the region of the crystal where 95% of the energy is deposited) for dose rates of 2.4 MGy/s (circles) and 40.3 MGy/s (triangles) at RT and of 40.3 MGy/s (squares) at 100 K. The dose at which the diffracted intensity decreased to one-half of its initial value (D1/2) was determined to be 0.36, 0.57, and 15.3 MGy for the RT series at 2.4 and 40.3 MGy/s and the cryo- series at 40.3 MGy/s, respectively.