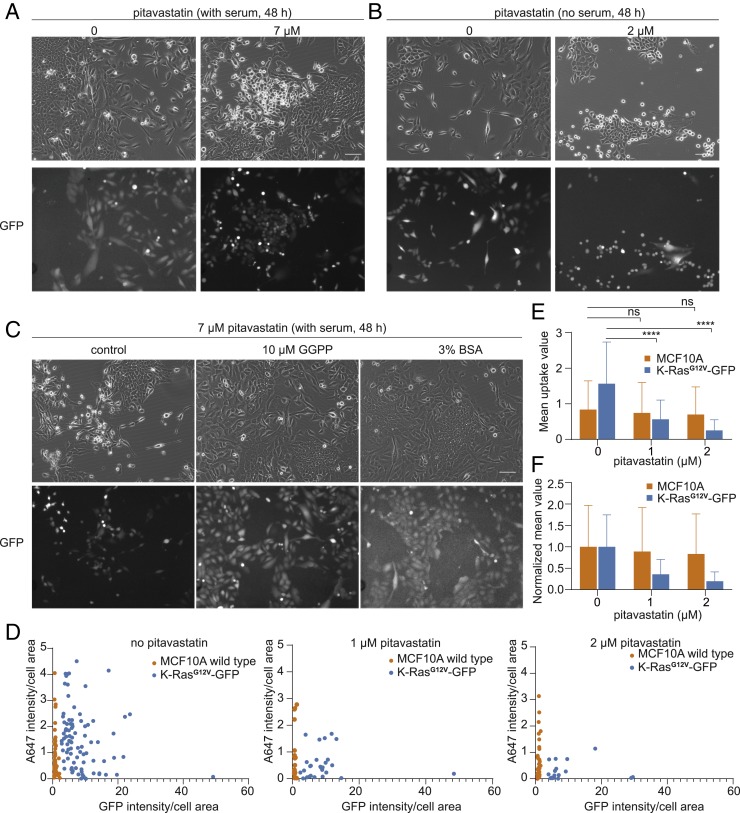
Fig. 7.
MCF10A cells expressing K-RasG12V-GFP are vulnerable to perturbation of the mevalonate pathway. (A) Cytotoxic effects of pitavastatin on MCF10A cells expressing K-RasG12V-GFP compared with wild-type cells in complete medium. Both MCF10A wild-type cells and RasG12V-GFP cells are included in the bright-field image. Only K-RasG12V-GFP cells are labeled in GFP images. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (B) Cytotoxic effects of pitavastatin on MCF10A cells expressing K-RasG12V-GFP compared with wild-type cells in serum-free medium. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (C) Supplementation of GGPP and BSA rescues pitavastatin-induced cell death in K-RasG12V-GFP cells. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (D) Measurement of fluid-phase uptake in MCF10A wild-type and K-RasG12V-GFP–expressing cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of pitavastatin. For each condition, a single cell is outlined for quantification; cells with less GFP signal are recognized as wild-type cells. (E) The mean value of fluid-phase uptake in MCF10A wild-type and K-RasG12V-GFP–expressing cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of pitavastatin (mean ± SD, n = 3 experiments, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey HSD test, ****P < 0.0001). (F) The normalized mean value of fluid-phase uptake in MCF10A wild-type and K-RasG12V-GFP–expressing cells in the presence of increasing concentrations of pitavastatin (mean ± SD).