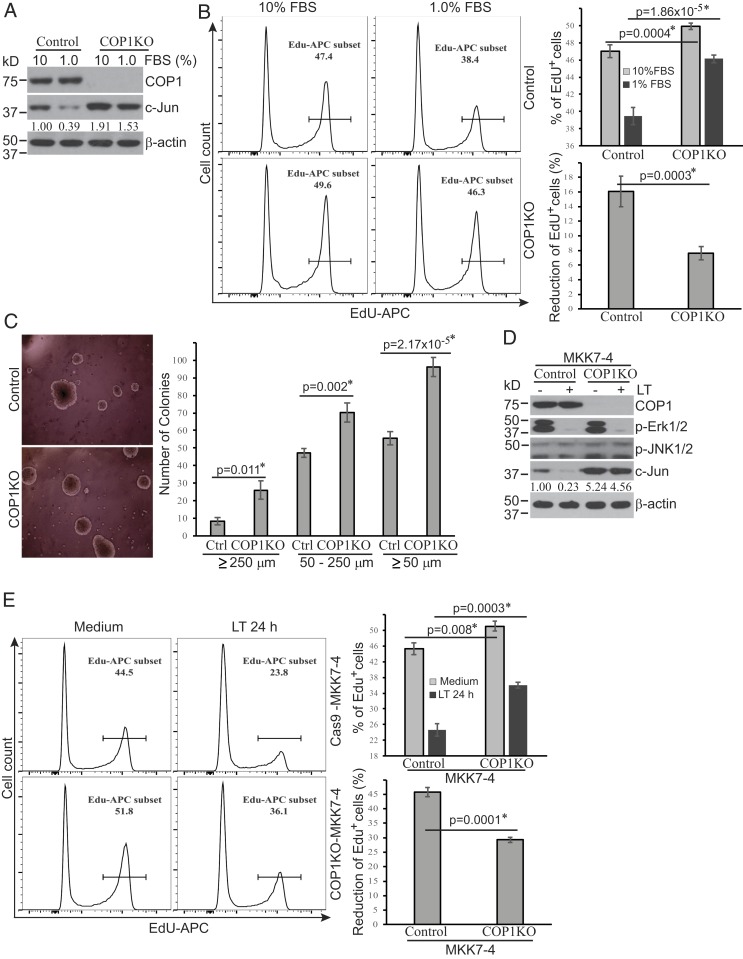
Fig. 5.
COP1-dependent pathways regulate cellular proliferation in suboptimal culture conditions. (A and D) COP1-deficient (COP1KO) and control Hepa1c1c7 cells (A) were cultured in media supplemented with 10% or 1% FBS for 24 h. COP1KO and control Hepa1c1c7 cells expressing MKK7-4 (D) were treated with LT for 2 h. Treated cells were analyzed for the expression levels of indicated proteins by Western blotting. c-Jun bands were quantified and normalized using β-actin. The relative amounts are shown under each band. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. (B and E) Cellular proliferation following culture in media containing 10% or 1% FBS for 24 h (B) or following treatment with or without LT for 24 h (E) was measured using the click-iT EdU cell proliferation kit and analyzed using flow cytometry and FlowJo software. Cell proliferation (EdU+) and proliferation reduction percentages were statistically analyzed using data from four (B) or three (E) independent experiments by an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test and presented as mean ± SE. Statistically significant differences were determined by P < 0.01. (C) COP1KO and Ctrl Hepa1c1c7 cells were cultured in soft agar for 2 wk. Colony photos shown are representative of three independent experiments (Left), and colony numbers presented represent mean ± SE from three independent experiments (Right). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test and significant difference was determined by P < 0.01.