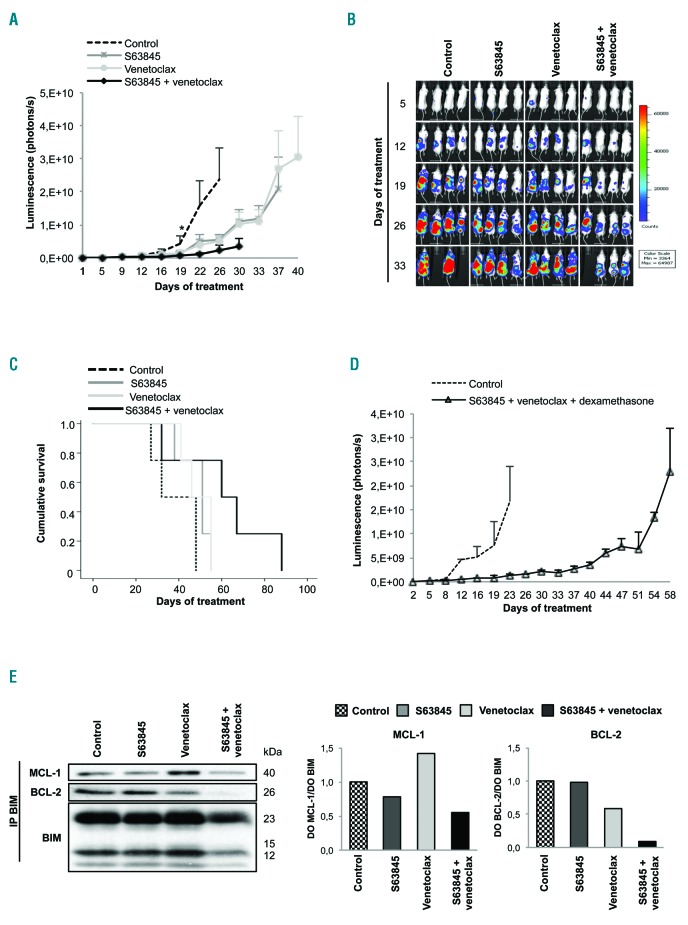
Figure 3.
The S63845 + venetoclax combination has potent in vivo anti-myeloma activity. (A) In vivo efficacy of S63845+venetoclax in an RPMI-8226-luc xenograft model of disseminated multiple myeloma (MM) in BRG mice. Experimental groups included: control (vehicle), S63845 (12.5 mg/kg intravenous, weekly), venetoclax (100 mg/kg oral administration, 5 days per week), and the respective combination (n=4 per group). Mice were treated until death or sacrifice for humane reasons. Statistically significant differences (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post-hoc comparisons, *P<0.05) were observed from day 19 onwards when comparing the combination with the control. Data are summarized as the mean±Standard Error of Mean (SEM). (B) Images representing the bioluminescence signal of each mouse by treatment group from day 5 to day 33 of treatment. (C) Kaplan-Meier curves representing the survival of each treatment group. (D) Efficacy of the triple combination S63845+venetoclax+dexamethasone using the doses and scheme as in (A) but with intraperitoneal dexamethasone administration (1 mg/kg, 2 days/week) (n=3 per group). Data are shown as mean±SEM. (E) RPMI-8226 cells were subcutaneously injected in CB17-SCID mice. When plasmacytomas reached 2 cm in one of their diameters, animals received one dose of vehicle, S63845 (12.5 mg/kg), venetoclax (100 mg/kg) or the respective combination (n=2 per group). Tumors were excised 24 hours after treatment and protein lysates from tumors were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-BIM antibody. MCL-1, BCL-2 and BCL-XL anti-apoptotic proteins bound to BIM were then analyzed by immunoblotting, quantified by densitometry analysis of bands normalized to those of BIM using ImageJ software, and represented in bar diagrams.