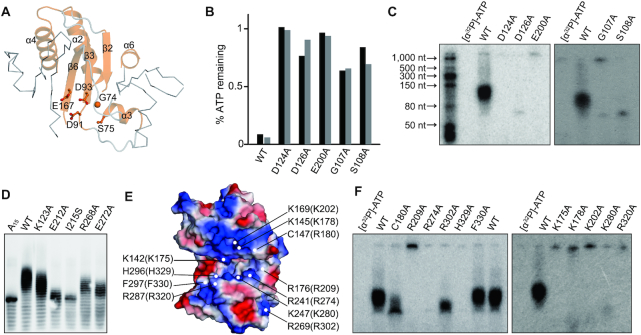
Figure 6.
Critical sites of FAM46B for polyadenylation activity. (A) The NTase core of FAM46B. The consensus NTase motif is highlighted as cartoon representation in orange. The conserved key residues are shown as sticks-and-ball models. (B) ATP consumption of mutants regarding key residues shown in A. Results from two independent experiments are presented. (C) AMP incorporation of mutants regarding residues shown in A. (D) Polyadenylation activity of human FAM46B mutants regarding residues located in the interface between NCD and HD. (E) Surface electrostatic potential of xtFAM46B. Conserved negatively charged residues that may be involved in RNA binding, together with two hydrophobic residues close to the catalytic center, are specified. Corresponding residues of human FAM46B are indicated in the parentheses. (F) AMP incorporation of mutants regarding residues shown in D.