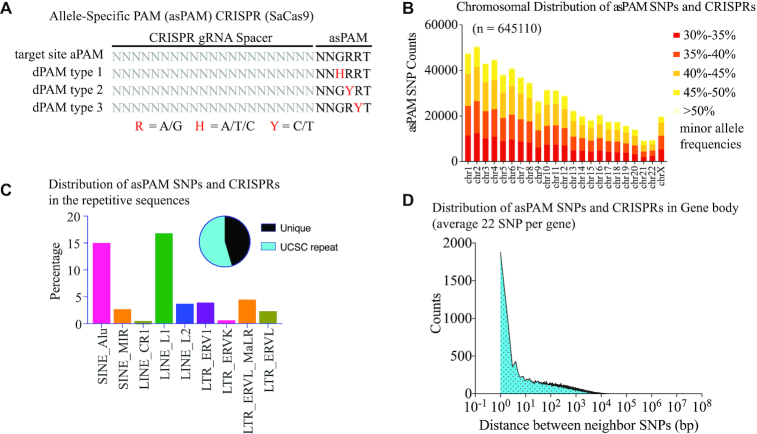
Figure 2.
Generation of a genome-wide high-frequency, allele-specific PAM-positioning (asPAM) SNP and CRISPR database. (A) Illustration of the SaCas9 CRISPR with active or dead PAMs. The reference and alternative allele of an asPAM SNP must fall in the GRR motif of a NNGRRT PAM and give rise to apposing PAM activities: active PAM (NNGRRT) and dead PAMs: NNHRRT, NNGYRT or NNGRYT. (B) Distribution of all SaCas9 asPAM SNP and CRISPRs across the human genome categorized by SNP frequency and chromosome. (C) Distribution of all SaCas9 asPAM SNP and CRISPRs in human repetitive sequences. Pie plot presents the distribution between asPAM SNPs located at unique and repetitive genome regions. (D) Distribution of distance between two adjacent SaCas9 asPAM SNPs within the gene body (including introns) + 5 kb flanking region.