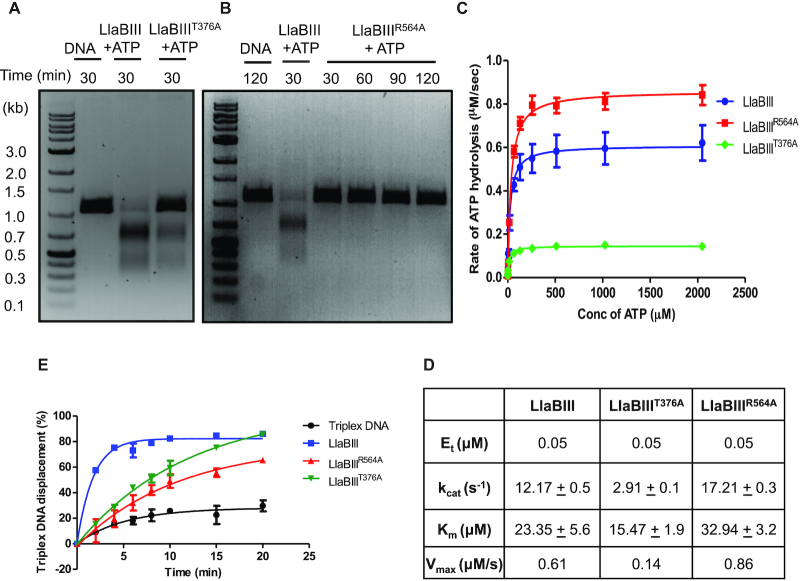
Figure 4.
Biochemical characterization of motifs III and V of LlaBIII ATPase domain. (A, B) DNA cleavage by LlaBIIIT376A and LlaBIIIR564A. In comparison to WT LlaBIII, LlaBIIIT376A shows less DNA cleavage activity while the motif V mutant LlaBIIIR564A is nucleolytically inactive. (C) The kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by WT LlaBIII (blue), LlaBIIIT376A (green) and LlaBIIIR564A (red). 50 nM LlaBIII or the mutants with 500 nM DNA concentration were used in NADH coupled ATPase assay. The ATP concentrations used were 0.25, 1, 4, 16, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024 and 2048 μM. Reactions were carried out at 25°C. Shown are the averages of three replicates. (D) Kinetic parameters for ATP hydrolysis obtained from (C). (E) Triplex displacement assay showing the percentage of triplex DNA displaced by LlaBIII (blue), LlaBIIIT376A (green) and LlaBIIIR564A (red) over different time points (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15 and 20 min) at 20°C. Black line is triplex DNA control showing the dissociation of TFO from the DNA in the absence of protein over the same time points. The reaction was performed with 4 mM ATP concentration. Shown are the averages of three replicates.