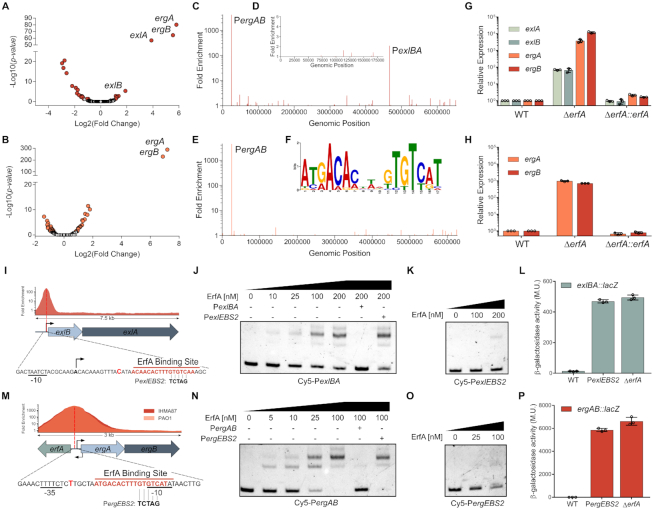
Figure 3.
ErfA directly regulates a second operon in addition to exlBA. (A andB) Volcano plots displaying the RNA-seq results of the genes differentially expressed in respective ΔerfA mutants versus IHMA87 (A) and PAO1 (B) wild-type strains. Genes with q-value < 0.05 are depicted in red (IHMA87) or orange (PAO1). (C–E) Enrichment of normalized mapped reads after ChIP-seq on the whole IHMA87 chromosome (C) and IHMA87 plasmid (D), and the PAO1 genome (E). (F) Enriched DNA motif obtained with MEME-ChIP on relevant ChIP-seq peaks corresponding to near-summit regions. (G and H) RT-qPCR analysis of ergA, ergB, exlA and exlB mRNA levels in wild-type, erfA mutant and complemented strains in IHMA87 (G) and PAO1 (H). Experiments were performed in triplicates, with RNA extracted from bacteria at OD600 = 1 in LB and normalized to the rpoD transcript. Error bars indicate the SD. (I) Enrichment of normalized mapped reads after ChIP-seq and location of ErfA binding site on the 7.5 kb region encompassing exlBA. Black arrows indicate transcription start sites. The position of the summit of the ChIP-seq peak is denoted as a bold bright red letter. Bases changed in the PexlEBS2 mutation of the binding site are shown. (J andK) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of ErfA on exlBA promoter (PexlBA). Recombinant ErfA-His10 protein (0–200 nM) was incubated with 0.5 nM Cy5-labeled PexlBA 80-mer probe (J) or the mutated Cy5-PexlEBS2 probe (K) for 15 min before electrophoresis. For competition assays, excess of unlabeled PexlBA or PexlEBS2 probes (100 nM) are denoted ‘+’ for the corresponding probe. (L) β-Galactosidase activities of the wild-type (WT) and ΔerfA strains harbouring exlBA::lacZ transcriptional fusion. The strain IHMA87exlBA::lacZ PexlBA-EBS2 carries the PexlEBS2 mutation indicated in I on ErfA binding site. Experiments were performed in triplicates, on bacteria in LB at OD600 = 1. Error bars indicate the SD. (M–P) These panels display the same experiments described in I,J,K,L, but focused on PergAB.