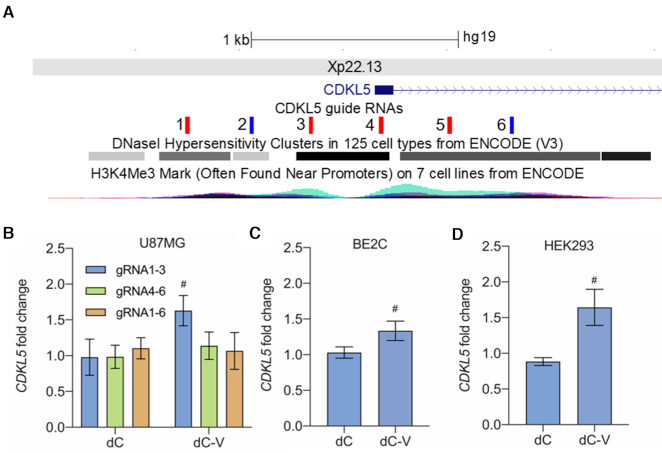
Figure 1.
Programmable transcription of the CDKL5 gene. (A) UCSC genome browser snapshot of the target sites of the six sgRNAs directed against the CDKL5 promoter on Xp22.13. DNase hypersensitive sites and H3K4me3, often found near promoters are derived from ENCODE. Sense sgRNAs are shown in blue, antisense sgRNAs in red. (B) CDKL5 mRNA fold change relative to mock-treated cells in U87MG cells determined by RT-qPCR resulting from programmable transcription using a dCas9-no effector (dC) or dCas9-VP64 (dC-V) in combination with different pools of three to six sgRNAs targeted to the CDKL5 promoter 48 h after transient transfection. #Significantly different from dCas9 sgRNAs 1–3, n = 3 independent experiments, Tukey's HSD, P < 0.05. (C) CDKL5 mRNA fold change relative to mock-treated cells in BE2C determined by RT-qPCR resulting from programmable transcription using dCas9-no effector or dCas9-VP64 co-expressed with sgRNAs 1–3 48 h after transient transfection. (D) CDKL5 mRNA fold change relative to mock-treated cells in Lenti-X 293T determined by RT-qPCR resulting from programmable transcription using dCas9-no effector or dCas9-VP64 co-expressed with sgRNAs 1–3 48 h after transient transfection. #Significantly different from dCas9 sgRNAs 1–3, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test P <0.05.