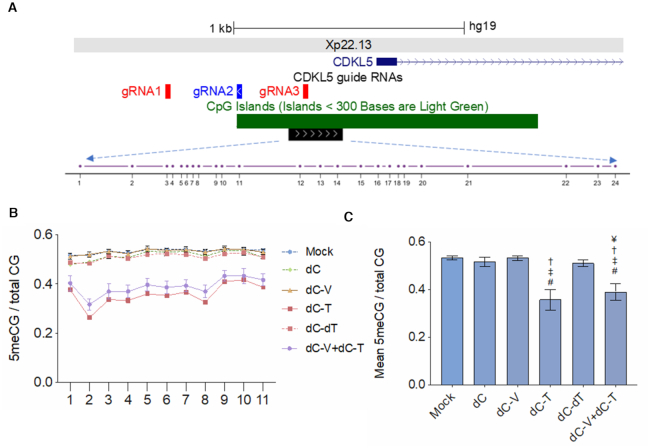
Figure 3.
dCas9-TET1CD causes removal of DNA methylation from the CDKL5 CGI promoter. (A) UCSC genome browser snapshot of the target sites of sgRNAs 1–3 directed against the CDKL5 promoter on Xp22.13 and a large CpG Island (>1 kb) spanning the transcriptional start site of CDKL5. The black box represents a >200 bp region assessed for targeted DNA methylation changes containing 24 individual CpG dinucleotides (drawn to scale). (B) 5-methylcytosine levels in a CpG context (5meCG) over total CpG context as assessed by targeted bisulfite sequencing across 11 CpG dinucleotides in mock-treated cells or cells transduced to constitutively express dCas9-no effector (dC) or dCas9 fused to either VP64 (dC-V) or TET1CD (dC-T), a combination thereof (dC-V+dC-T) or a catalytically inactive TET1CD (dC-dT). X-axis depicts the individual CpG position relative to the amplicon (not drawn to scale). (C) Mean 5-methylcytosine levels in a CpG context over all 11 CpG dinucleotides in all treatment groups. #Significantly different from mock-treated cells, ‡significantly different from dCas9, †significantly different from dC-dT, ¥significantly different from dC-T, n = 3 independent experiments, Tukey's HSD, all P < 0.05.