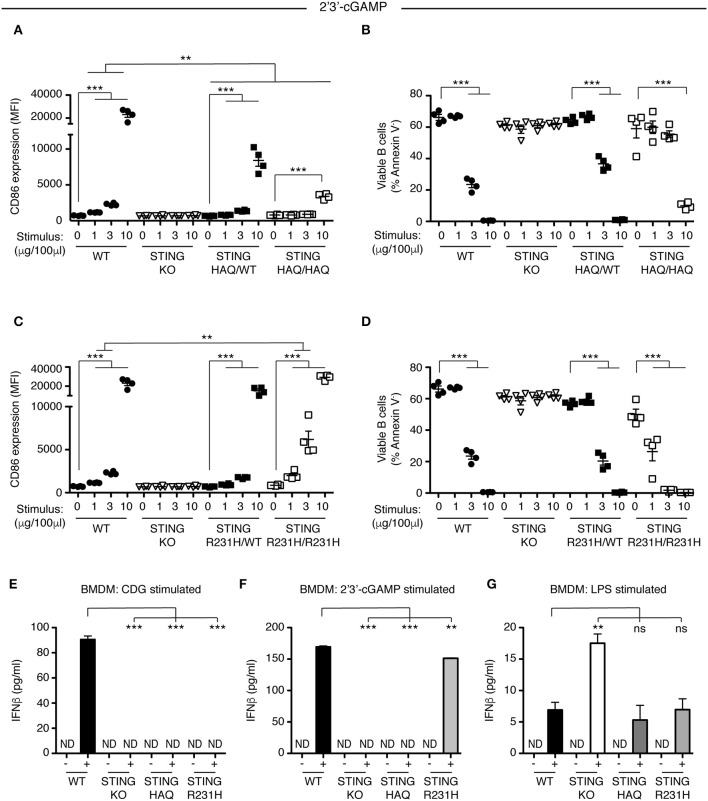
Figure 4.
STING-HAQ expressing cells but not STING-R231H expressing cells are impaired in their response to endogenous 2′3′ cGAMP. (A,B) WT, STING KO, STING-HAQ/WT, and STING-HAQ/HAQ B cells (n = 4) were cultured for 18 h with the indicated concentrations of 2′3′ cGAMP. (A) CD86 expression (MFI, gated on B220+ Annexin V−) and (B) survival (% Annexin V−) of B cells stimulated with 2′3′ cGAMP. (C,D) WT, STING KO, STING-R231H/WT, and STING-R231H/R231H B cells (n = 4) were cultured for 18 h with the indicated concentrations of 2′3′ cGAMP. (C) CD86 expression (MFI, gated on B220+ Annexin V−) and (D) survival (% Annexin V−) of B cells stimulated with 2′3′ cGAMP. (E–G) Bone-marrow derived macrophages generated (n = 3) from WT, STING KO, STING-HAQ/HAQ, and STING-R231H/R231H mice were incubated with 10 μg/ml CDG (E), 10 μg/ml 2′3′ cGAMP (F) or 100 ng/ml LPS (G) for 5 h and the concentration of IFNβ in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. Data shown are representative of at least two independent replicate experiments. Bars in (A–D) represent mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were made for each stimulus concentration and the range of concentrations that reached statistical significance between genotypes are indicated by horizontal lines above the graph. ND: not detected, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 using an unpaired Student's t-test.