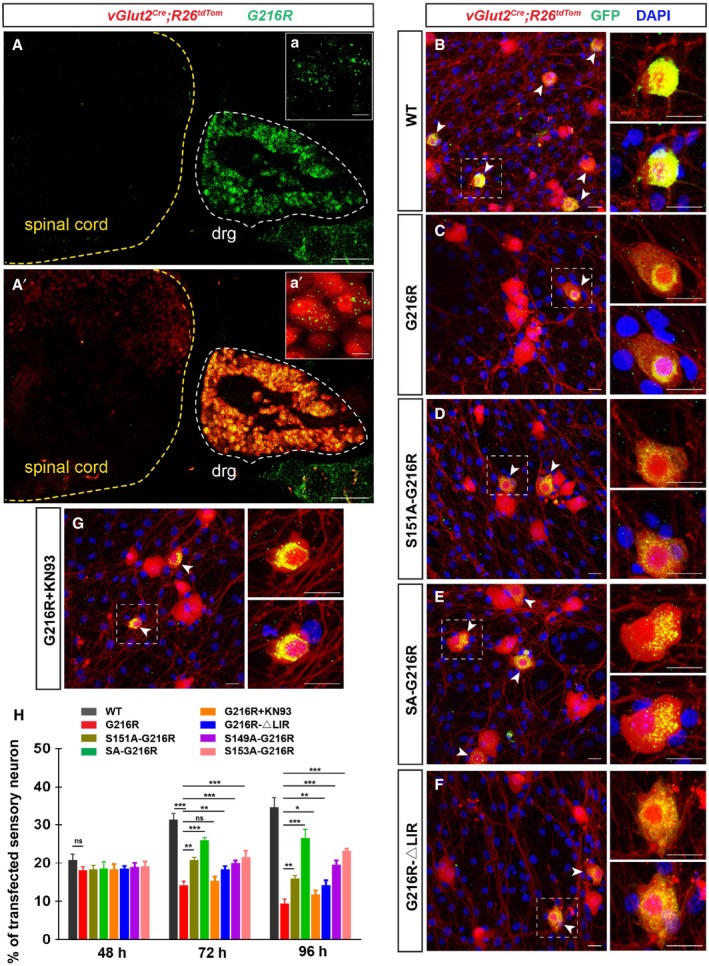
-
A, A’
Specific expression of FAM134B mRNA (green) in sensory neurons (red) of P4d vGlut2
Cre
;R26
lsl‐tdTom mouse. Scale bars, 100 μm. The white dotted line indicates the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) where sensory neurons are genetically labeled with Tomato. Insets of (a) and (a’) are high magnifications of sensory neurons showing the colocalization of FAM134B mRNA and Tomato. Scale bars, 10 μm.
-
B–G
Cultured sensory neurons from DRGs of E14.5 vGlut2
Cre
;R26
lsl‐tdTom embryos were infected with same titers of recombinant lentivirus expressing GFP‐FAM134B WT (B), G216R (C), S151A‐G216R (D), SA‐G216R (E), G216R‐ΔLIR (F), and G216R supplemented with 5 μM KN93 (G), respectively. Infected sensory neurons (GFP+/Tom+) are indicated with arrowheads. The nuclei of all cells are shown with DAPI staining. Scale bars, 20 μm.
-
H
Quantification of the viability of sensory neuron after 48, 72, and 96 h of infection. Sensory neuron viability was calculated as the percentage of transfected sensory neuron (GFP+/Tom+) in total sensory neurons (Tom+). For each time point, four biological replicates were included for statistical analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two‐way ANOVA; error bars indicate SEM. “ns” is the abbreviation for “not significant”. For all of the groups, at least 10 fields of the slides were included.