-
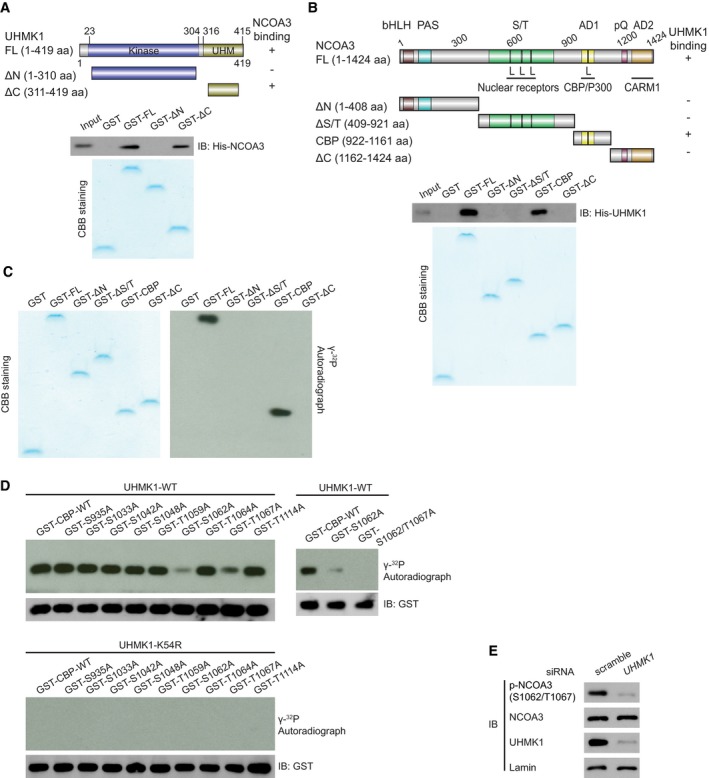
A
GST‐UHMK1 full length (FL), GST‐UHMK1 ΔN (N‐terminal truncated, 1–310aa), and GST‐UHMK1 ΔC (C‐terminal truncated, 311‐419aa) were constructed (upper panel). GST‐labeled FL, ΔN, and ΔC protein fragments were incubated with His‐NCOA3. Pull‐down, Coomassie blue staining, and Western blotting were performed (lower panel).
-
B
GST‐NCOA3 full length (FL), GST‐NCOA3 ΔN (1–408aa), GST‐NCOA3 ΔS/T (409–921aa), GST‐NCOA3 CBP (922–1,161aa), and GST‐NCOA3 ΔC (1,162–1,424aa) were constructed (upper panel). Pull‐down assay with GST‐NCOA3 FL or its protein fragments (ΔN, ΔS/T, CBP, and ΔC) and His‐UHMK1 were performed (lower panel).
-
C
We performed an in vitro kinase assay by incubating purified NCOA3 FL or its protein fragments with purified UHMK1 kinase. These proteins were visualized using Coomassie blue staining. The phosphorylation of the substrates is shown in the autoradiograph.
-
D
WT‐UHMK1 or kinase‐dead UHMK1‐K54R protein was mixed with GST‐CBP‐WT or the indicated mutant, and in vitro kinase assays were performed.
-
E
Silencing UHMK1 in SGC7901 cells via UHMK1‐siRNA. NCOA3 phosphorylation at S1062/T1067 was measured with a special Ab that recognizes phosphorylated NCOA3‐S1062/T1067.