-
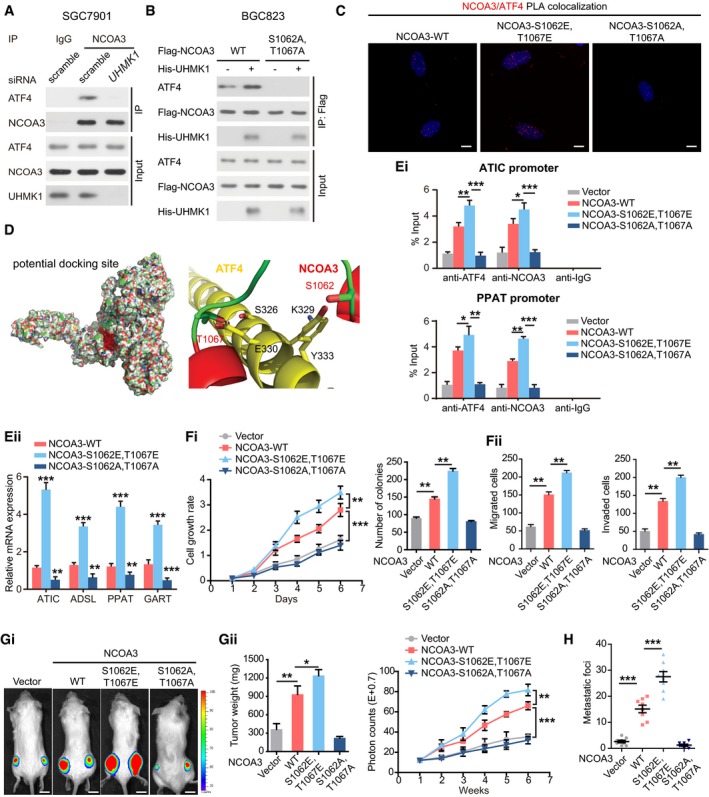
A
Knockdown of UHMK1 blocked NCOA3 binding to ATF4. SGC7901 cells were treated as indicated. Co‐IP was carried out with mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) or anti‐NCOA3 antibody. Then, Western blotting was performed.
-
B
BGC823 cells were transfected with Flag‐NCOA3 or NCOA3‐S1062A/T1067A with or without His‐tagged UHMK1. Co‐IP was performed using an anti‐Flag antibody.
-
C
Proximity ligation assay of the interaction between different NCOA3 proteins and ATF4 in BGC823 cells. Confocal images were acquired with a Nikon A1 microscope and the Nikon Elements software suite. Maximum projection images are shown (original magnification ×120). Scale bars = 20 μm.
-
D
Computational molecular docking analysis to investigate the molecular mechanism by which NCOA3‐S1062/T1067 phosphorylation is involved in the interaction of NCOA3 binding to ATF4. Based on the predictions of ZDOCK software, S1062 and T1067 of NCOA3 are located in the interface between ATF4 and NCOA3, and S1062/T1067 phosphorylation greatly enhances the binding affinity of NCOA3 for ATF4 by increasing NCOA3 hydrophilicity.
-
E
(Ei) ChIP data from BGC823 cells are presented as indicated. (Eii) NCOA3‐S1062/T1067 phosphorylation by UHMK1 enhanced the expression of critical genes as indicated (three biological replicates).
-
F
(Fi and Fii) The effects of WT‐NCOA3 and the NCOA3‐S1062A/T1067A, and NCOA3‐S1062E/T1067E mutants on BGC823 cell proliferation, invasion, and migration (three biological replicates).
-
G, H
The effects of WT‐NCOA3, and the NCOA3‐S1062A/T1067A, and NCOA3‐S1062E/T1067E mutants on GC growth and metastasis in the mouse model (n = 10 mice/group). Scale bars = 1 cm.
Data information: Unpaired two‐tailed statistical significance was assessed by Student's
‐test. Data represent mean ± SD. *
< 0.001.