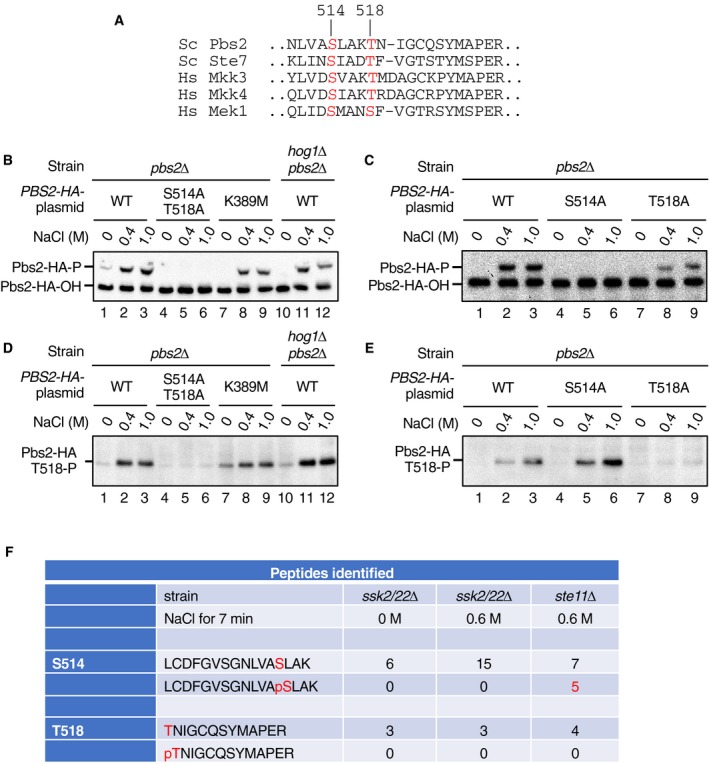
Figure EV3. Detection of the activating phosphorylation at S514 and T518 in Pbs2.
-
AAlignment of the amino acid sequences around the activating phosphorylation sites in yeast (Sc) and human (Hs) MAP2Ks. Those residues that are phosphorylated by the cognate MAP3Ks are highlighted in red. Numbers refer to the positions in Pbs2. Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Hs, Homo sapiens.
-
B, CDetection of Pbs2 S514 phosphorylation by the Phos‐tag band‐shift assay. The yeast strain KT003 (pbs2Δ) or YM105 (hog1Δ pbs2Δ) was transformed with YCplac22I’‐PBS2‐HA (a single‐copy plasmid that encoded C‐terminally HA‐tagged Pbs2 [Pbs2‐HA] expressed from the PBS2 promotor) or its indicated derivatives and was treated with the indicated concentrations of NaCl for 5 min. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated using anti‐HA antibody 3F10 and were subjected to Phos‐tag SDS–PAGE. Pbs2‐HA was detected by immunoblotting using anti‐HA antibody F‐7. Positions of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated Pbs2‐HA (Pbs2‐HA‐P and Pbs2‐HA‐OH, respectively) are indicated.
-
D, EDetection of Pbs2 T518 phosphorylation by anti‐P‐T518 immunoblotting. Cell extracts were prepared as in (B) and (C) and were analyzed by standard SDS–PAGE, and immunoblotted for phosphorylated T518 using the anti‐P‐T518 antibody.
-
FMass spectrometric (MS) analysis of Pbs2 phosphorylation. The SHO1 branch‐only strain TM280 (ssk2/22Δ pbs2Δ) or the SNL1 branch‐only strain KT005 (ste11Δ pbs2Δ) was each transformed with pRS414‐FLAG‐Pbs2. These cells were either unstimulated (0 M NaCl) or stimulated with 0.6 M NaCl for 7 min, and affinity‐purified FLAG‐Pbs2 was subjected to MS analyses. Numbers of detected peaks that corresponded to the tryptic peptides containing a Pbs2 activating phosphorylation site, either phosphorylated or unphosphorylated, are tabulated.
Source data are available online for this figure.
