Fig. 1.
Angiotensin synthesizing enzymes and precursors are expressed in human stellate ganglia.
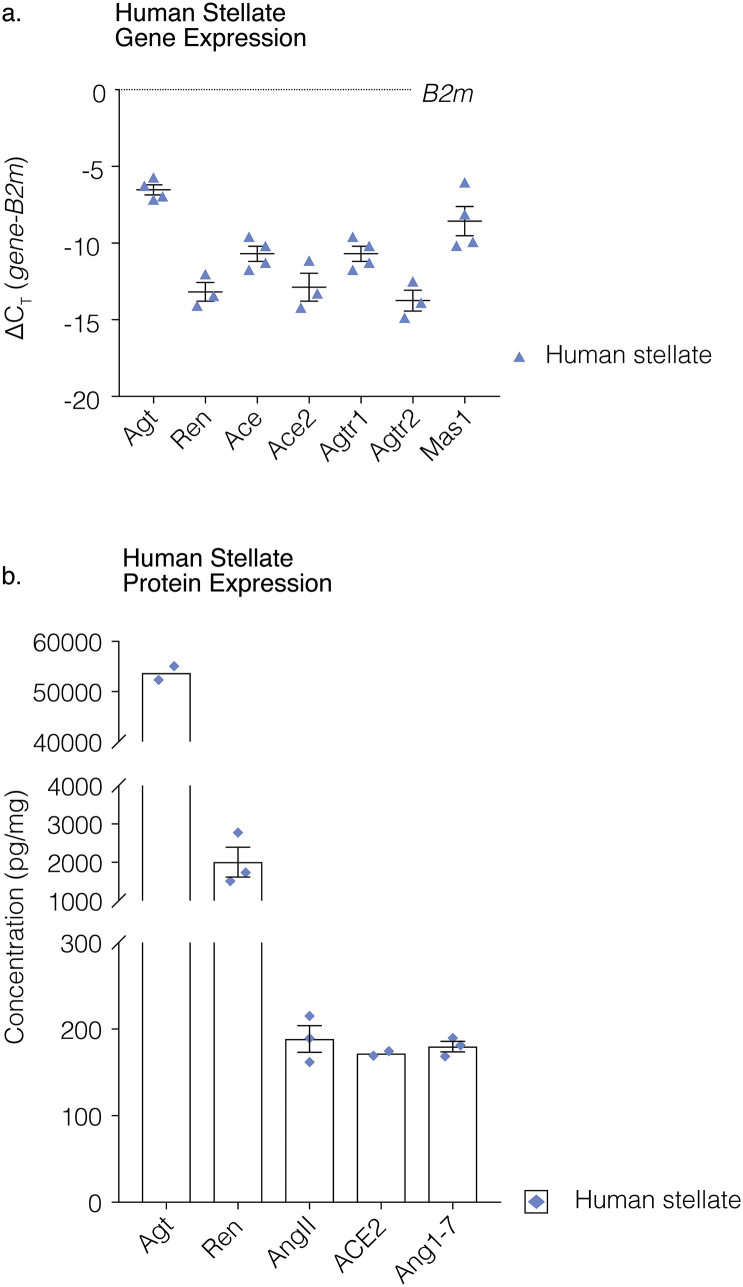
In human stellate ganglia the presence of the mRNA transcripts encoding Agt (n = 4), Ren (n = 3), Ace (n = 4), Ace2 (n = 3), Agtr1 (n = 4), Agtr2 (n = 3) and Mas1 (n = 4) were confirmed by qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR raw counts for the genes of interest were normalized to the control gene B2m using the ∆CT method and expressed as ∆CT mean ± SEM (a). ELISAs were used to demonstrate the protein expression of the relevant proteins of interest including Agt, Ren, AngII, ACE2 and Ang1–7 in human stellate ganglia. Agt was found to be highly expressed in human stellate ganglia (n = 2, ~53,694 pg/mg), as was Ren (n = 3, 2005 ± 388 pg/mg). AngII (n = 3, 188.7 ± 15.37 pg/mg), ACE2 (n = 2, 171.9 ± 2.60 pg/mg) and Ang1–7 (n = 3, 179.9 ± 6.13 pg/mg) were also identified and were found to have similar levels of expression (b). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. A model diagram depicts AngII and Ang1–7 release from the stellate ganglia and the proposed pre-and post-synaptic effects.