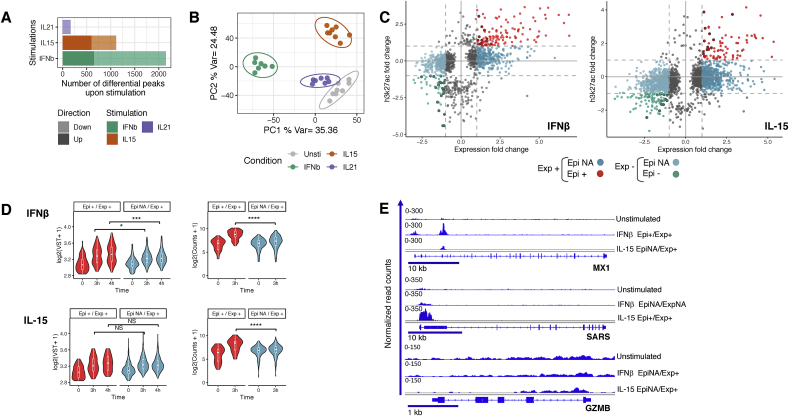
Fig. 3.
Specific epigenomic profiles induced by alarmins and adaptive cytokine. All the differential H3K27ac peaks after 3 h of stimulation with IFNβ, IL-15 or IL-21 (FDR ≤ 0.01) are depicted in (A) barplots and (B) used for PCA to depict epigenetic responses of IE-CTLs upon stimulation. (C) Scatter plot displaying the association between changes in H3K27ac (Y-axis) and expression (X-axis) upon stimulation. Gene-peak pairs were grouped based on the direction of the fold change in expression (Exp+ and Exp-) and the direction (or lack of changes) in H3K27ac after stimulation (Epi+, Epi - and Epi NA). Red dots (Epi + Exp+) indicate a fold change >1 in both expression and H3K27ac occupancy. Green dots (Epi- Exp-) indicate a fold change < 1 in both expression and H3K27ac occupancy. Dark blue (Exp + EpiNA) and light blue (Exp- EpiNA) are gene-peak pairs with fold change >1 or <1 in expression, respectively, and no change in H3K27ac. (D) Violin plots showing the distribution of gene expression levels (left, log2(VST+1)) and H3K27ac occupation (right, log2(Counts+1)) in up-regulated genes responding to IFNβ (upper panel) and IL-15 (lower panel) stimulation. Upregulated genes with H3K27ac |fold change| >1 (Epi+/Exp+) are shown in red and those without H3K27ac changes (EpiNA/Exp+) are shown in blue. Significant differences were assessed by Wilcoxon test (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.01; ****p < 0.001, NS non-significant). (E) Representative H3K27ac tracks illustrating the concordance between epigenomics and gene expression after IFNβ or IL-15 treatment. n = 8 samples per time point and condition. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)