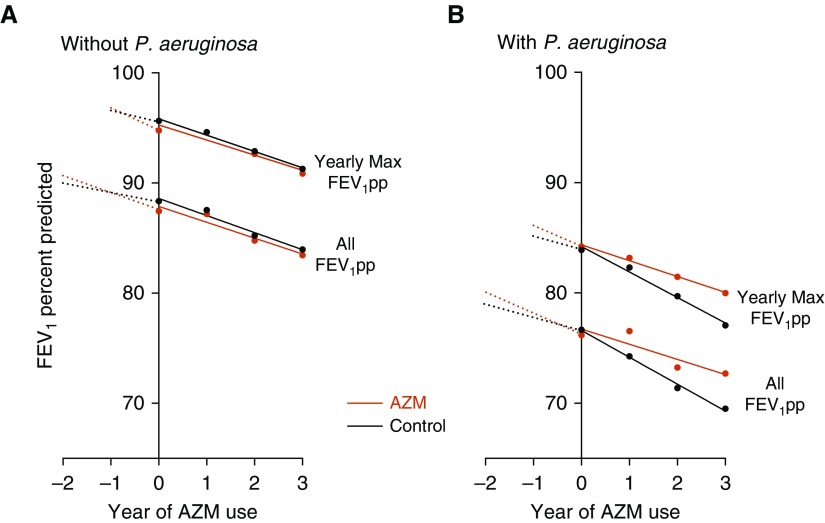
Figure 1.
(A and B) FEV1% predicted (FEV1pp) over 3 years (using all data and, separately, only yearly maximum) after incident chronic azithromycin (AZM) versus control among those without Pseudomonas aeruginosa (A) and those with P. aeruginosa (B). Estimates for all data were derived from the model allowing individual trends per year.