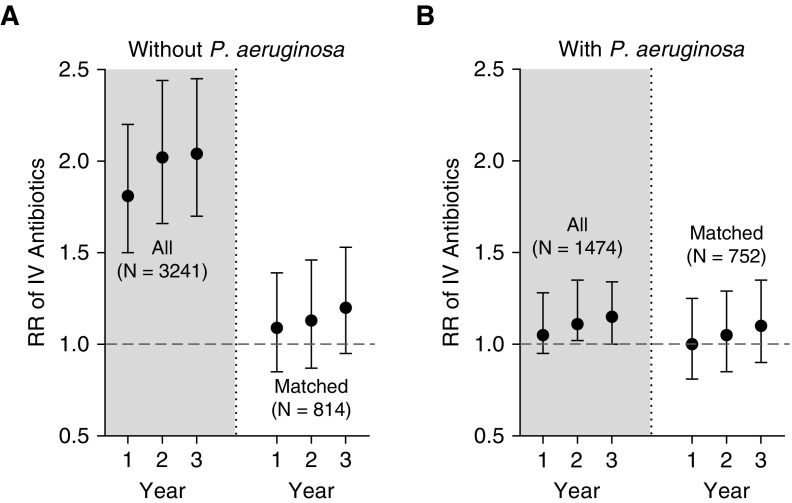
Figure 2.
Relative risk (RR) of pulmonary exacerbations treated with intravenous (IV) antibiotics among those with incident chronic use of azithromycin (AZM) versus controls. Shaded regions show all identified patients (not propensity score matched), and unshaded areas show the propensity score–matched cohorts. (A) Those without Pseudomonas aeruginosa and (B) those with P. aeruginosa. Figure represents high AZM users relative to low AZM users, and RR > 1.0 indicates greater use of IV antibiotics.