FIG. 4.
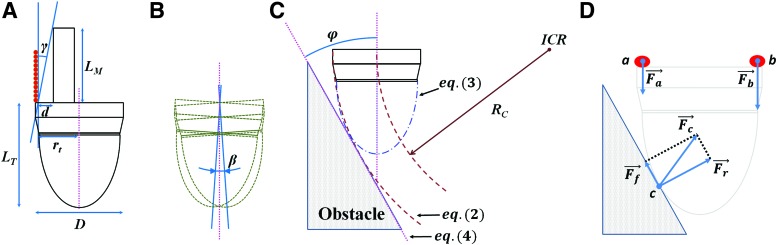
(A) Main parameters of tip and growing mechanism: tip diameter D = 48 mm; tip length LT = 62 mm (h = 22 mm and e = 40 mm); length of the taller component assembled in the growing mechanism LM = 48 mm; distance of the taller component from the internal side of the built structure d = 10 mm; and distance of the tip center from the internal side of the built structure rt = 22 mm. (B) Tip oscillation induced during the circular deposition of material. Amplitude of this oscillation depends from material thickness; in our case, with a filament of 1.7 mm diameter, the amplitude β is ∼2°. (C) Drawing of the tip facing the obstacle with maximum angle φ, characterized by a curvature of the growing robot with minimum radius RC = 98.2 mm (ICR is the center of rotation). (D) Close view of the tip–obstacle interaction with the forces involved. When considering a simple 2D model, the extruder can be localized in either of the two points: a, where a force Fa should be exercised to extrude the material, or b, where the extrusion force is Fb. The tip enters in contact with the obstacle at a certain point c, where the friction force Ff and the reaction force Fr are localized and contribute in the resulting force Fc. 2D, two-dimensional. Color images are available online.