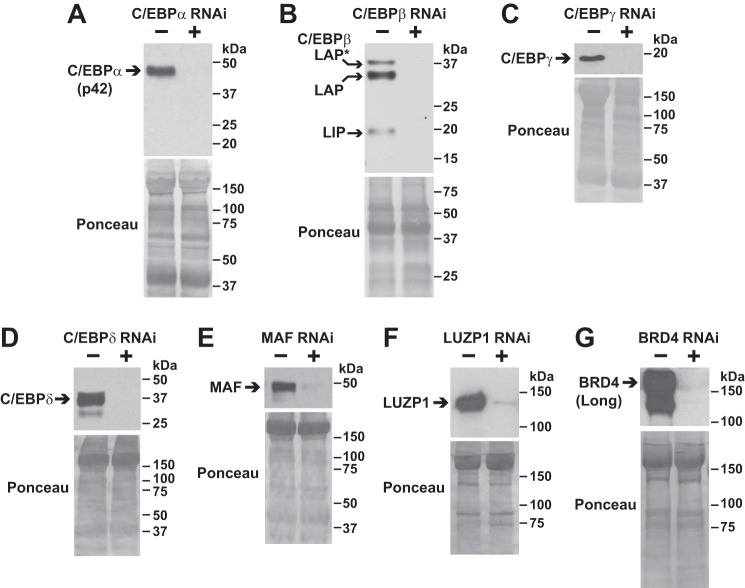
Figure 3.
Development of RNAi constructs that target ATF4 interactors in mouse skeletal muscle fibers. Mouse TA muscles were co-transfected with 10 μg of cDNA (C/EBPα plasmid in A; C/EBPβ plasmid in B; C/EBPγ plasmid in C; C/EBPδ plasmid in D; MAF plasmid in E; LUZP1–FLAG plasmid in F; and BRD4–FLAG plasmid in G) plus either 20 μg of nontargeting control RNAi plasmid or 20 μg of RNAi plasmid targeting C/EBPα (A), C/EBPβ (B), C/EBPγ (C), C/EBPδ (D), MAF (E), LUZP1 (F), or BRD4 (G), as indicated. Seven days post-transfection, bilateral TA muscles were harvested for SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using rabbit monoclonal anti-C/EBPα IgG (A), mouse monoclonal anti-C/EBPβ IgG (B), rabbit polyclonal anti-C/EBPγ antibody (C), rabbit polyclonal anti-C/EBPδ antibody (D), rabbit polyclonal anti-MAF antibody (E), and HRP-conjugated mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG IgG (F and G). Membranes were stained with Ponceau S to confirm equal loading.