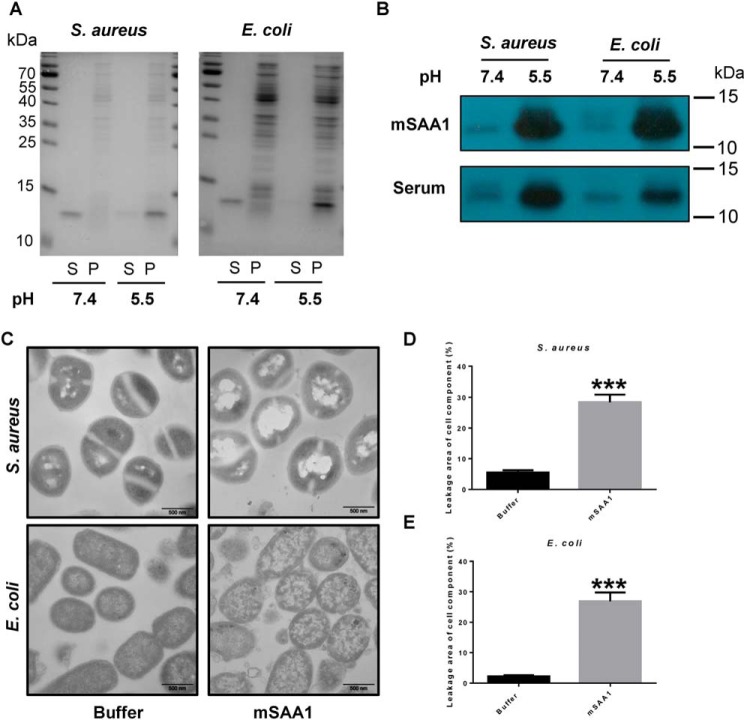
Figure 2.
SAA binds bacteria and disrupts its cell membrane at low pH. A, binding of mSAA1 to E. coli or S. aureus was incubated with 5 μm recombinant mSAA1 in 10 mm sodium phosphate, 150 mm NaCl buffer, pH 5.5 or pH 7.4. After centrifugation, the supernatant (S) and the pellet (P) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. B, binding of mSAA1 to E. coli or S. aureus was incubated with 10% AgNO3-injected mice serum in 10 mm sodium phosphate, 150 mm NaCl buffer, pH 5.5 or pH 7.4. After centrifugation, SAA in the pellet was detected by immunoblotting. C, transmission EM micrographs of E. coli and S. aureus cells were incubated with 10 μm mSAA1 or buffer. (scale bar, 500 nm). D and E, cell component leakage areas of S. aureus (D) and E. coli (E) cells (n = 30) were incubated with 10 μm mSAA1 or buffer. Significant differences versus control group are indicated by asterisks: ***, p < 0.001. Error bars, S.E.M.