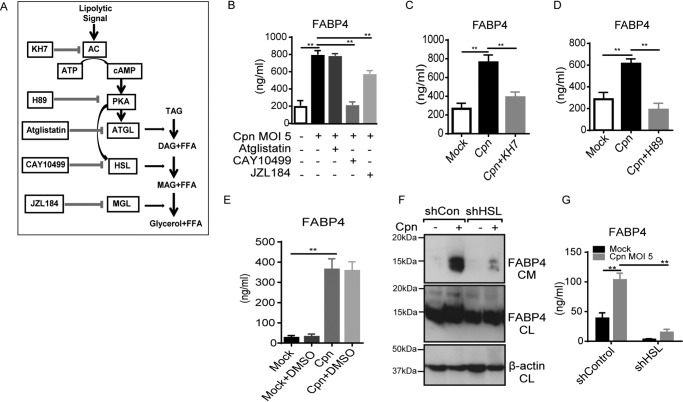
Figure 2.
C. pneumoniae infection–induced FABP4 secretion is regulated by cAMP–PKA–HSL pathway. A, the lipolytic pathway inhibitors used in this experiment. B–E, FABP4 levels were measured in the cultured medium of 3T3-L1 adipocytes at 24 h after Cpn infection at a MOI of 5 in the presence or absence of atglistatin (50 μm), CAY10499 (50 μm) or JZL184 (1 μm) (B), KH7 (50 μm) (C), H89 (50 μm) (D), or DMSO 1% solvent control (E). F and G, 3T3-L1 adipocytes differentiated from 3T3-L1 preadipocyte lines each stably expressing a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against mRNAs encoding either murine EGFP (control) or HSL were infected with Cpn MOI 5 for 24 h. F, immunoblot analysis of FABP4 in the cultured medium (CM) and cell lysates (CL) of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. β-Actin served as the standard. G, secretion of FABP4 in cultured medium of these 3T3-L1 adipocytes was examined by ELISA (n = 3/group; B–E and G). **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA (B–E); two-way ANOVA (G). The data are shown as the means ± S.E. and are representative of at least three experiments. AC, adenylyl cyclase; PKA, protein kinase A; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; TAG, triacylglycerol; DAG, diacylglycerol; MAG, monoacylglycerol; FFA, free fatty acid.