Figure 4.
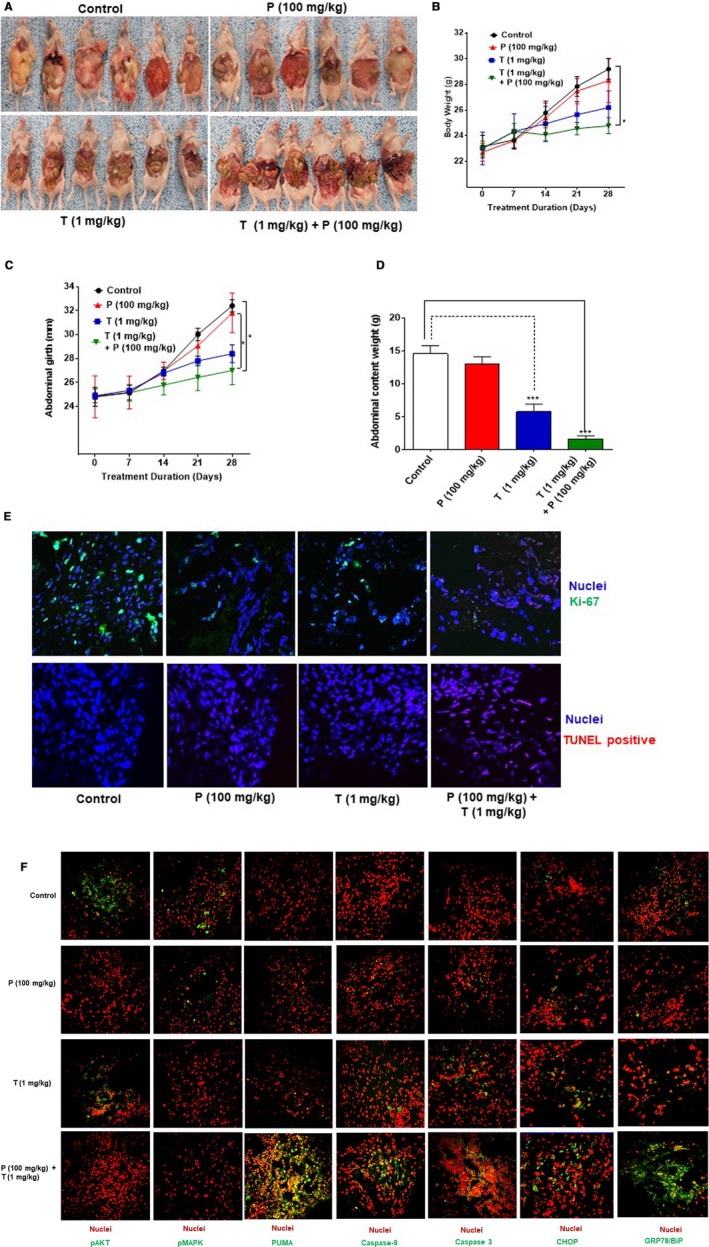
Dual drug therapy reduced mucinous tumor growth in vivo: Patient‐derived xenografts were treated with PBS alone (control), or pictilicsib (P) alone (100 mg/kg b.w.), or trametinib (T) alone (1 mg/kg b.w.), or combination of P + T every other day (starting on day 7 following tumor implantation) until they were euthanized at day 28. Gross intra‐abdominal tumor burden is depicted pictorially (A). Weekly measurements of body weight (g) (B) and abdominal girth (mm) (C) were recorded. At the time of sacrifice abdominal contents weight (tumor + organs, in grams) was quantified (D). Harvested tumor tissue from euthanized mice was stained with proliferation marker (Ki67 IF assay) antibody and TUNEL assay was also performed (E). IF assay was performed for signaling pathway proteins (pAKT and pMAPK), ERS protein levels (GRP78/BiP and CHOP) and apoptosis proteins (Caspase 3/9 and PUMA) following 3 weeks of drug therapy (F). Error bars represent standard error of the mean among the 6 xenograft specimens. Asterisk represents a statistically significant difference compared with the control group (*P < .05, ***P < .001)
