Figure 1. Approaches to Prevent LOS Caused by Expansion of Gut Pathobiont K. pneumoniae in Neonatal Mice.
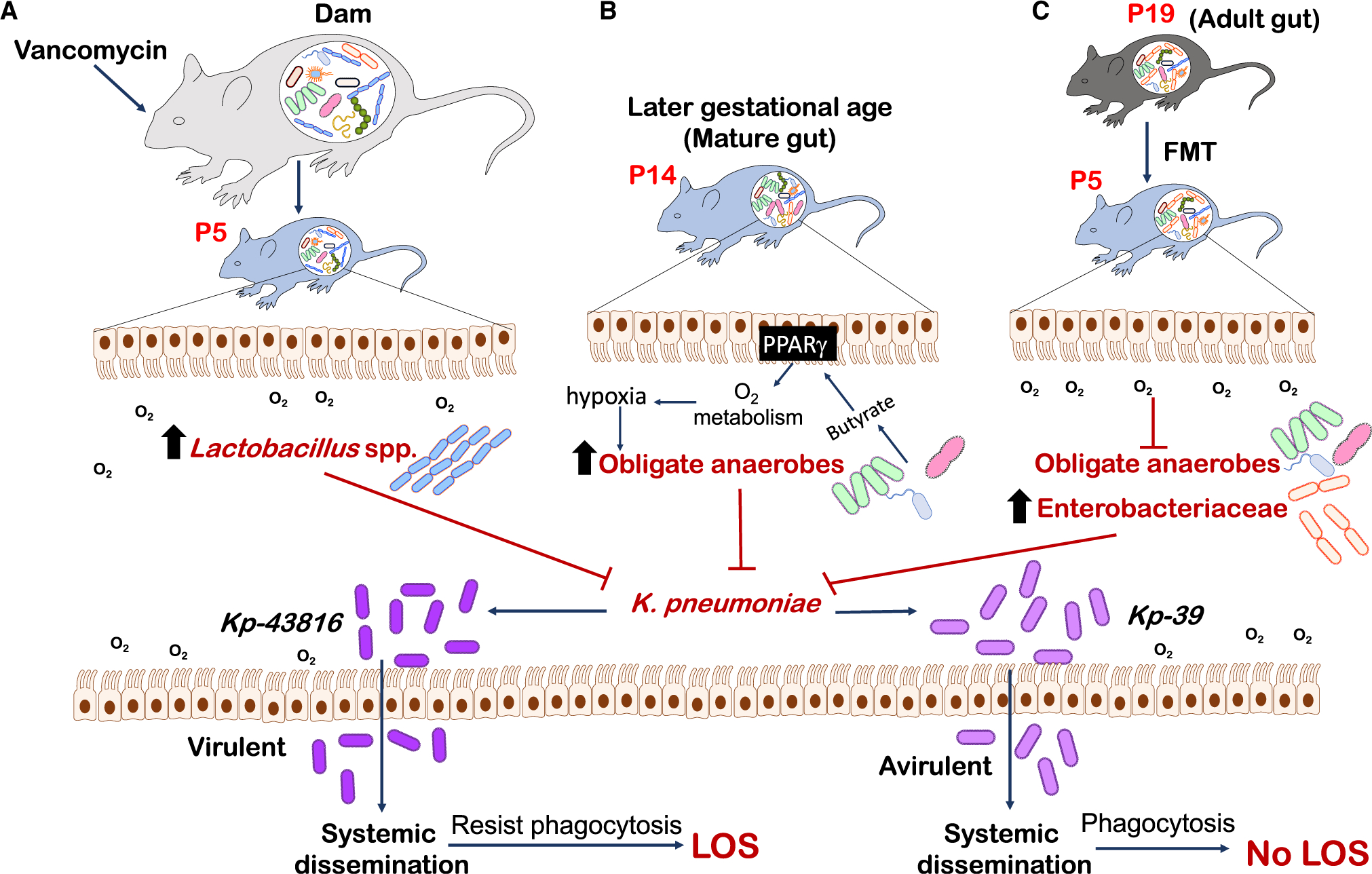
Singer et al., (2019) demonstrated three approaches to K.pneumoniae expansion in the neonatal gut that prevent LOS: (A) administration of the antibiotic vancomycin to maternal dams to increase the expansion of Lactobacillus species in the neonatal gut; (B) a hypoxic environment to support growth of obligate anaerobes in a mature gut (P14); and (C) expansion of Enterobacteriaceae species facilitated by higher oxygen levels in the neonatal than in the mature gut after FMT of adult gut microbiome (P19). Approaches (A)–(C) allow for the expansion of specific gut bacteria (Lactobacillus murinus, obligate anaerobes, and Enterobacteriaceae, respectively) that exert colonization resistance against the pathobiont K. pneumoniae to diminish LOS in neonates.
