Figure 1. The effects of insulin and glucagon on hepatic metabolism.
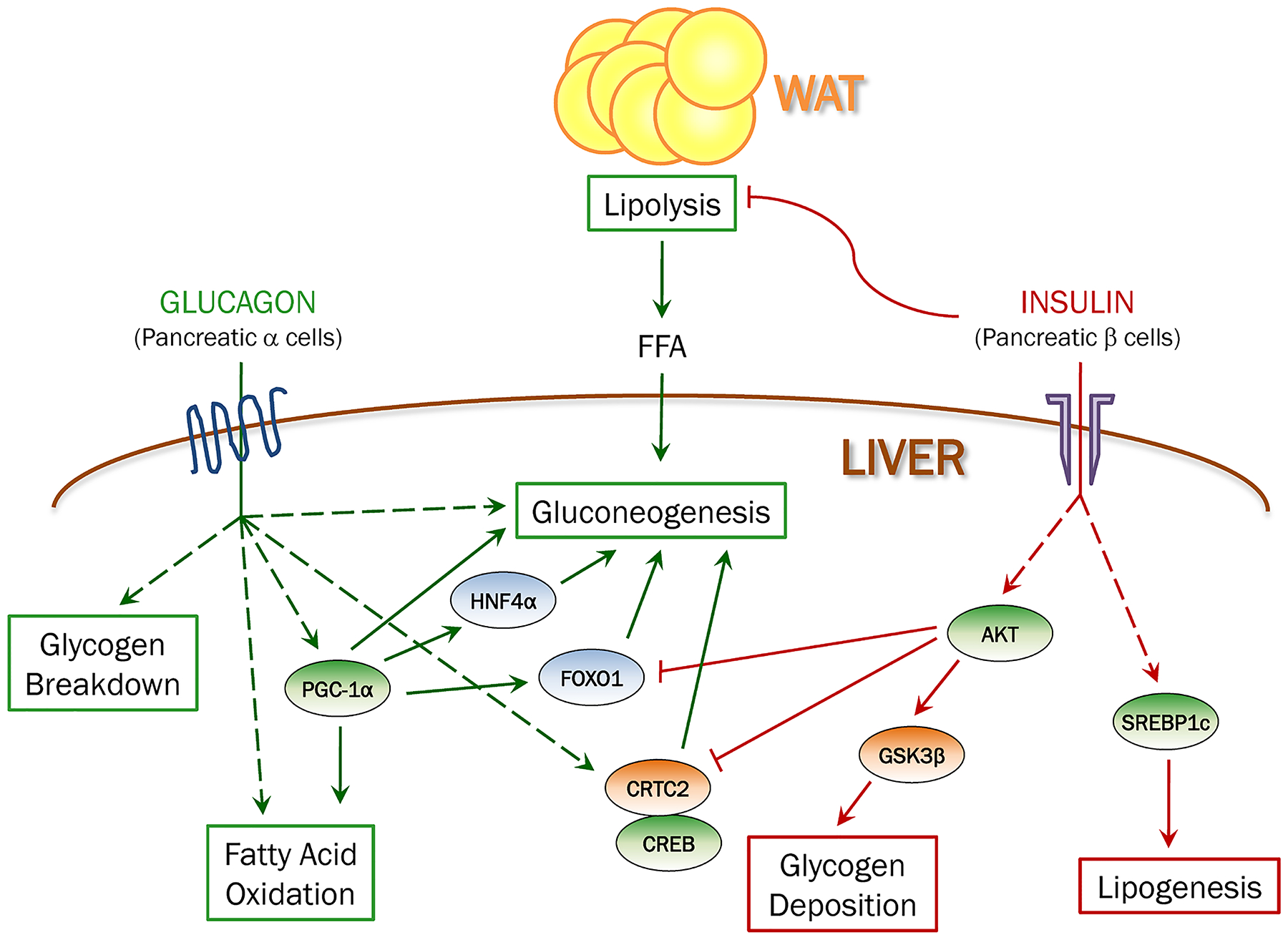
Insulin suppresses hepatic glucose production both directly by inhibiting glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis, and indirectly by inhibiting lipolysis in fat and limiting free fatty acids (FFA) supply to liver. In addition, insulin strongly stimulates glycogenesis and lipogenesis. Glucagon promotes hepatic glucose production by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Glucagon also has catabolic effects in liver by promoting fatty acid oxidation.
