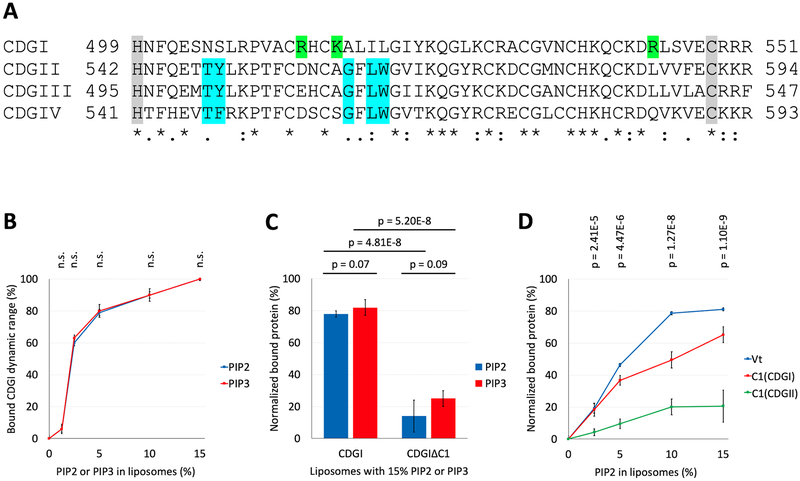
Figure 3: The C1 domain of CDGI associates with the phosphoinositides, PIP2 and PIP3.
(A) Sequence comparison of the human CDG isoforms. Numbers correspond to the residue positions in the full-length proteins. Gray shading highlights the C1 domain boundaries. Complete (*) or partial (: and .) conservation of the residues are indicated. Blue shading indicates critical residues needed for DAG/phorbol ester binding by typical C1 domains of CDGII, CDGIII and CDGIV28,29. Green shading indicates positively charged residues (R513, K516 and R543) present only in the atypical C1 domain of CDGI. (B) Co-sedimentation assays using liposomes, formed from PC (60%) and PE (25%) plus molar equivalent compensating amounts of PS between (15% to 0%) and PIP2 or PIP3 (0% to 15%), show concentration dependent CDGI association profiles for both PIP2 and PIP3. The amount (%) of bound CDGI corresponds to the dynamic range based normalized values obtained by subtracting the scaled basal level binding by non-PIP2/PIP3 liposome components. The error bars correspond to SD, n=3. (C) Association of CDGI with either PIP2 or PIP3 is significantly reduced upon C1 domain deletion. Data are shown for liposomes containing 15% PIP2 or PIP3 along with 60% PC and 25% PE, but lacking PS. The amount (%) of bound protein corresponds to the normalized values obtained by subtracting the scaled basal level binding by non-PIP2/PIP3 components. The error bars correspond to SD (6 experimental replicates). (D) Concentration dependent association of PIP2 is observed for the Vinculin tail (Vt) domain (positive control) and the C1 domain of CDGI, but not that of CDGII. The amount (%) of bound protein corresponds to the normalized values obtained by subtracting the scaled basal level binding by non-PIP2 liposome components. The error bars correspond to SD (3 experimental replicates for Vt, 6 experimental replicates for C1(CDGI) and C1(CDGII)).