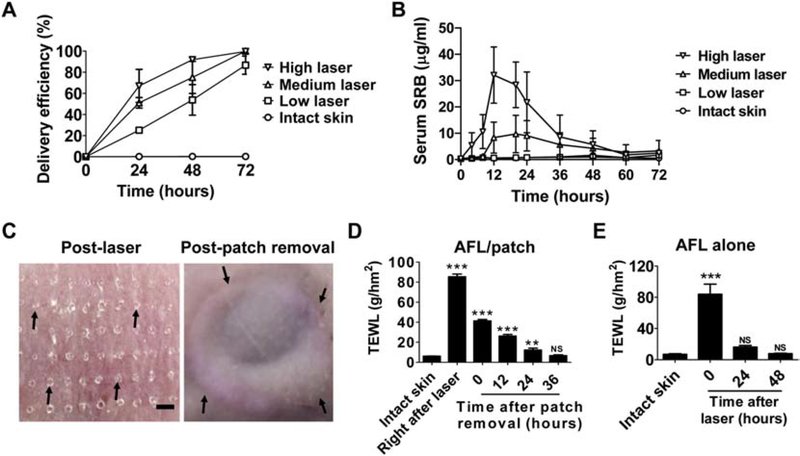
Fig. 2. AFL-assisted 3-day sustained SRB delivery in vivo.
A. Powder SRB-coated reservoir patches were topically applied onto AFL-treated or intact skin of BALB/c mice. Patches were removed daily for 3 days to evaluate the delivery efficiency. n=4–5. B. Powder SRB-coated reservoir patches were topically applied onto AFL-treated skin or intact skin of BALB/c mice followed by patch removal 3 days later. A small amount of blood was collected at different time points (3, 6, 9, 12, 16, 20, 26, 32, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60 and 72 hours) to quantify serum SRB levels. C. Lateral back skin of BALB/c mice was exposed to AFL (2.5 mJ/5%) followed by topical application of powder SRB-coated reservoir patches. Patches were removed 3 days later. Skin pictures were taken right after AFL treatment (left) and patch removal (right). Arrows in the left panel pointed to AFL-generated skin MCs. Arrows in the right panel pointed to the boundaries of reservoir patch application. Scale: 667 μm. D. Lateral back skin of BALB/c mice was exposed to AFL (2.5 mJ/5%) followed by topical application of powder SRB-coated reservoir patches as in C. Patches were removed 3 days later. TEWL was measured before and right after AFL treatment, right after and at different time points after patch removal. E. Lateral back skin of BALB/c mice was exposed to AFL (2.5 mJ/5%). TEWL was measured before AFL treatment or at different time points after AFL treatment. n=4–5. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test was used to compare differences between groups in D and E. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. NS: not significant.