Figure 1: General mechanisms of lncRNA function.
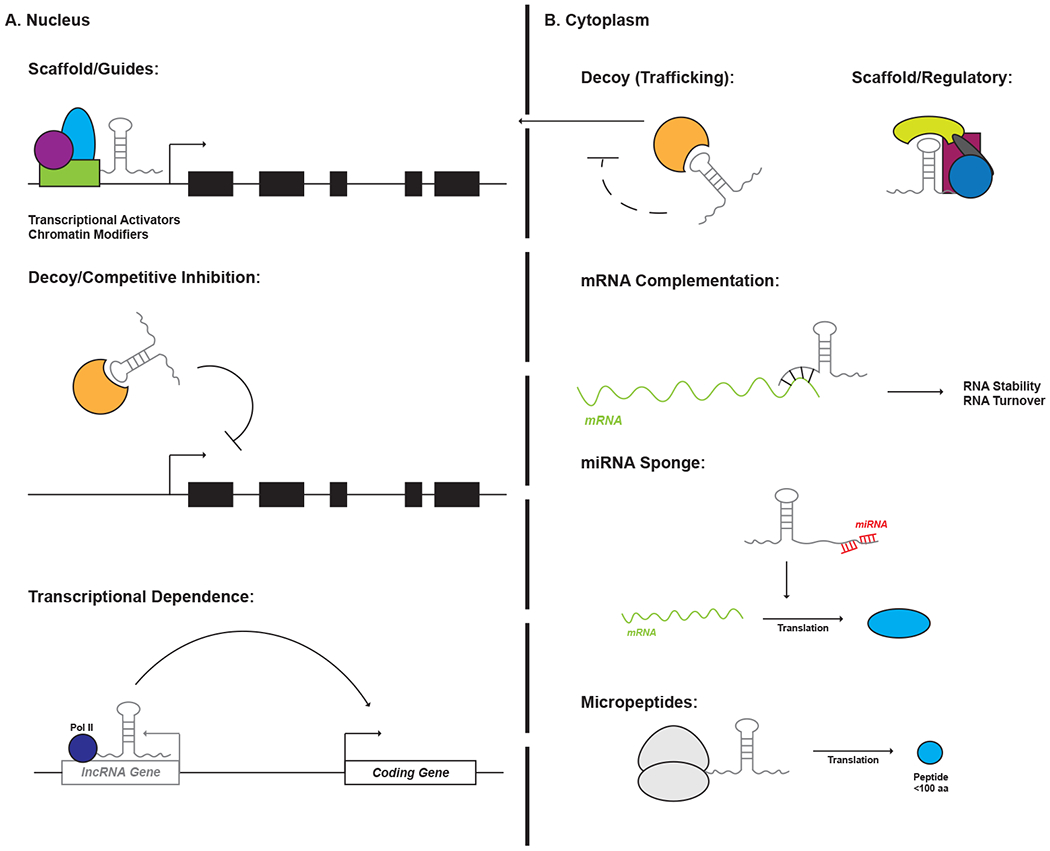
LncRNAs exhibit extensive versatility in regulating transcription and translation within a cell. These modes of action can be delineated in part by the intracellular compartment in which a lncRNA resides. The majority of nuclear lncRNAs function by regulating transcription initiation. This can be accomplished via interactions with proteins such as epigenetic modifiers and transcription factors to either recruit or inhibit these effectors from binding to target loci within the genome. In some cases, the lncRNA itself is dispensable and transcription through a lncRNA gene is what is required for transcription of a neighboring, coding locus. Cytoplasmic lncRNAs function to directly modulate protein function or affect transcript stability. Moreover, some cytoplasmic lncRNAs may encode short open reading frames that produce functional micropeptides of <100 amino acids.
