Figure 2: LncRNAs in innate immune signaling.
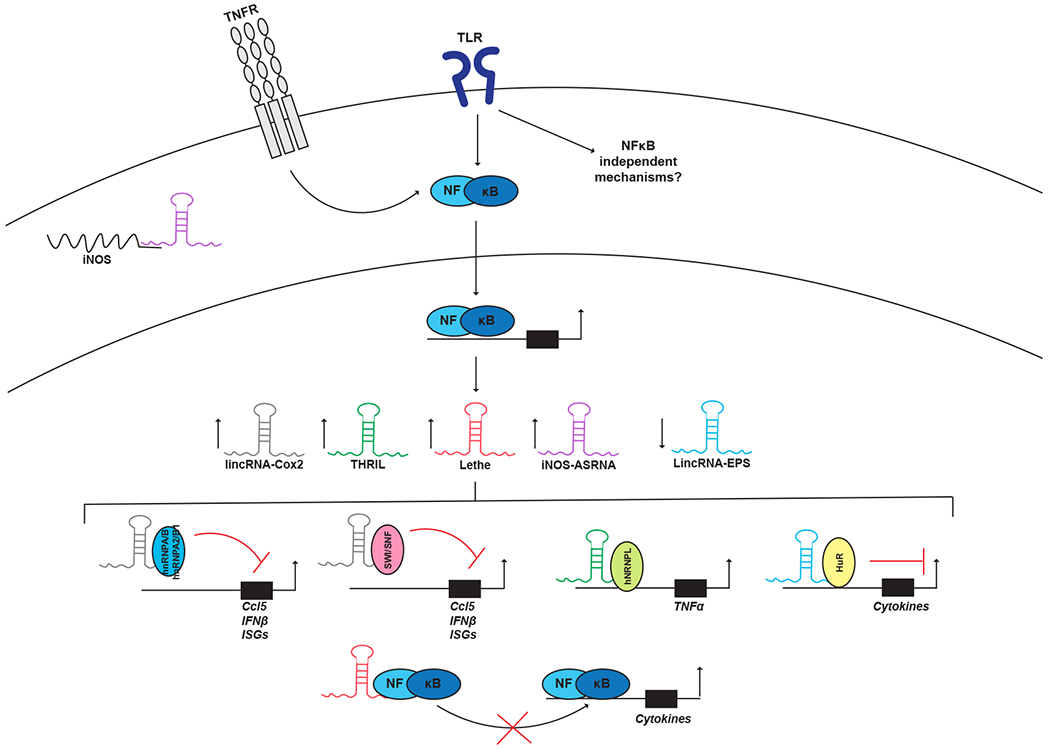
TLR stimulation leads to dynamic changes in the expression of a number of lncRNAs some of which function within the context of innate immunity. LincRNA-Cox2 acts to both activate and repress cytokines via interactions with SW/SNF or hnRNPA/B/hnRNPA2/B1 respectively. THRIL recruits hnRNPL to the Tnfa locus to promote transcription. LincRNA-EPS serves as a negative regulator of several inflammatory genes by recruiting hnRNPL. The iNOS-ASRNA is upregulated by IL-1β stimulation and localizes to the cytoplasm where it promotes the stability and subsequent translation of the iNOS coding transcript through direct base-pair complementation. Lethe is induced by TNFα signaling and functions as a decoy molecule, inhibiting NFκB function. Although the examples illustrated in the figure have focused on NFκB-associated lncRNAs there are like many other lncRNAs which regulate alternative signaling pathways associated with other transcription factors. Additional focus on lncRNA studies will likely reveal these important regulators.
