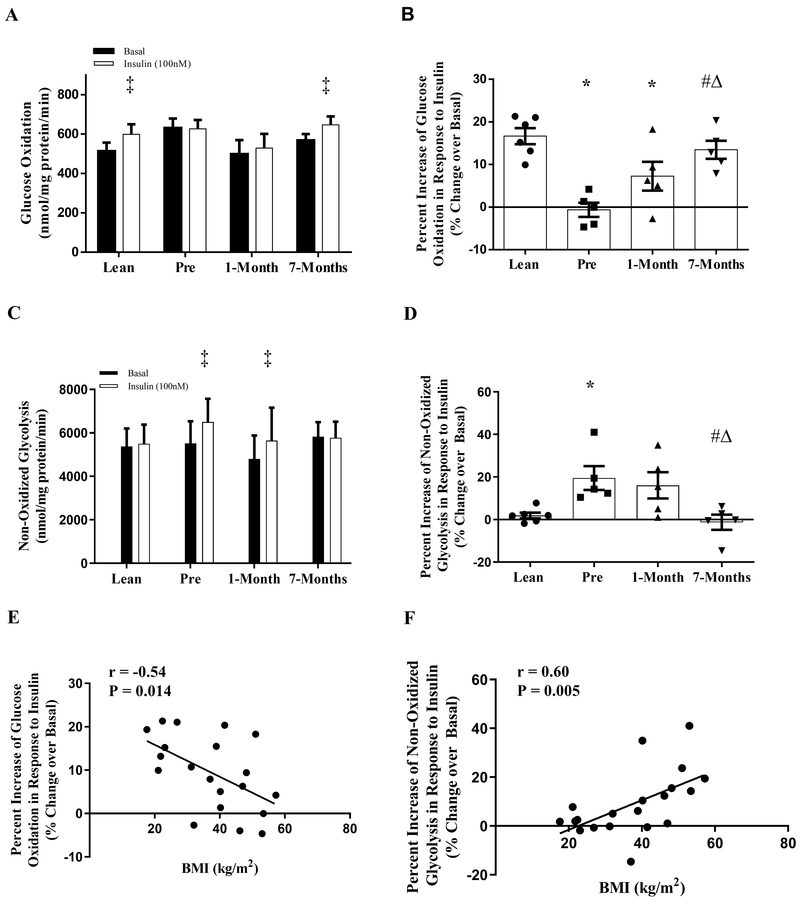
Figure 1:
Glucose partitioning in primary human myotubes derived from lean and severely obese humans before (Pre), 1-month, and 7-months after RYGB surgery. (A) Glucose oxidation under basal and insulin-stimulated conditions. (B) Percentage change of glucose oxidation in response to insulin stimulation. (C) Non-oxidized glycolysis under basal and insulin-stimulated conditions. (D) Percentage change of non-oxidized glycolysis in response to insulin stimulation. (E) Correlation BMI and percentage change of glucose oxidation in response to insulin stimulation. (F) Correlation between BMI and percentage change of non-oxidized glycolysis in response to insulin stimulation. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 6, Lean; n = 5, Pre, 1-month, and 7-months post-RYGB. ‡ P < 0.05 vs. Basal; * P < 0.05 vs. Lean; # P < 0.05 vs. Pre; Δ P < 0.05 vs. 1-month.