Figure 3.
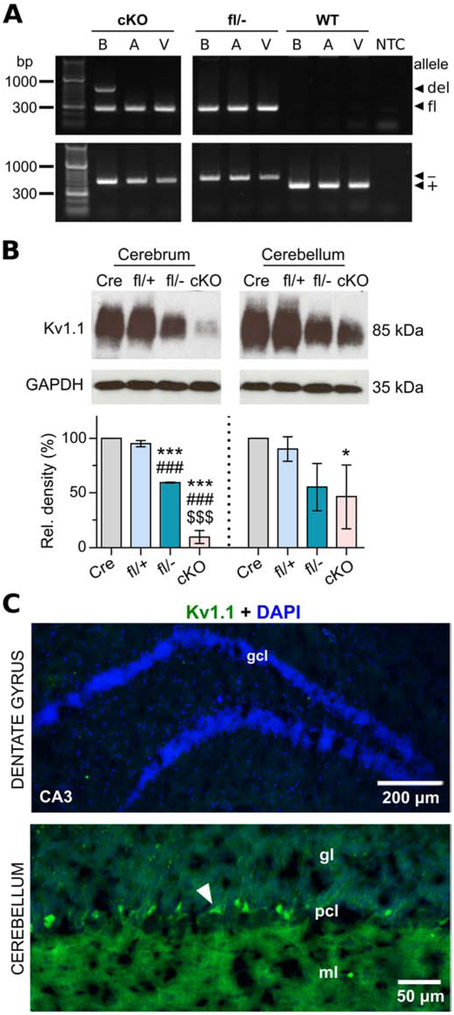
Molecular and immunohistochemical characterization of neuron-specific Kcna1 cKO mice. A, PCR detection of the Kcna1 deletion (del; 679 bp), floxed (fl; 260 bp), null (−; 337 bp), and WT (+; 475 bp) alleles from genomic DNA isolated from brain (B), atrium (A), and ventricle (V) of cKO mice and Kcna1fl/− and WT controls. NTC, no template control. B, Representative Western blots for Kv1.1 and GAPDH loading control from the cerebrum and cerebellum of hemizygous Syn-Cre (Cre), heterozygous Kcna1 floxed (fl/+), compound heterozygous Kcna1 floxed/null (fl/−), and neuron-specific Kcna1 cKO (cKO) mice (1-2 months old) with corresponding quantification of Kv1.1 protein levels (n=3/genotype). C, Immunohistochemistry and fluorescence imaging in cKO mice reveals an absence of anti-Kv1.1 immunoreactivity (green) in the dentate gyrus but persistent expression in the cerebellum. However, the intensity of staining in basket cell terminals (white arrowhead) appeared less intense than Kcna1fl/+ mice. CA3, Cornu Ammonis of the hippocampus; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; gcl, granule cell layer; gl, granular layer; ml, molecular layer; pcl, Purkinje cell layer. *P < 0.05 vs. Cre; ***P < 0.0001 vs. Cre; ###P < 0.0001 vs. fl/+; $$$P < 0.0001 vs. fl/− (1-way ANOVA; post-hoc Tukey test).