Figure 4.
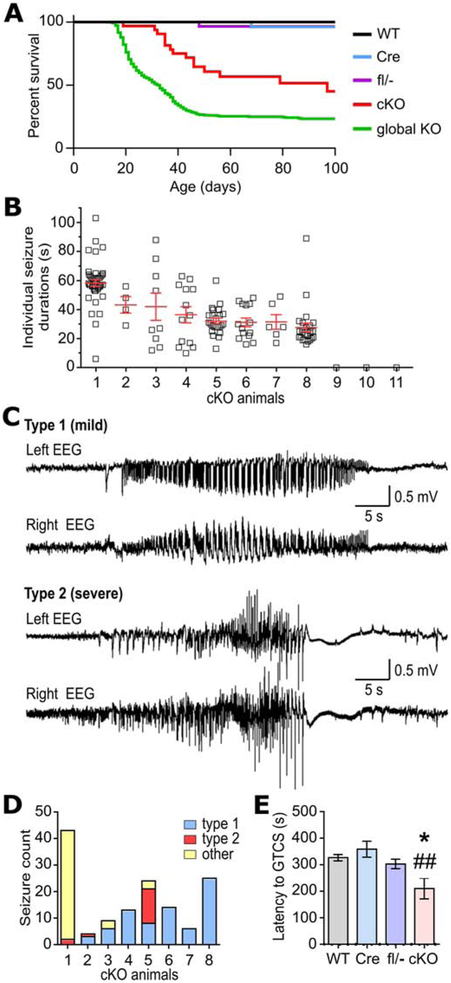
Premature death and seizure phenotypes in neuron-specific Kcna1 cKO mice. A, Kaplan-Meier survival curves for WT (n=50), hemizgous Syn1-Cre (Cre; n=36), compound heterozygous Kcna1 floxed/null (fl/−; n=32), neuron-specific Kcna1 cKO (cKO; n=32), and global Kcna1 knockout (global KO; n=553) mice. In cKO mice, survival was significantly decreased compared to Cre, fl/−, and WT controls (P < 0.0001, Log-rank test) but significantly increased compared to global KO mice (P = 0.0002, Log-rank test). B, Plot of individual seizure durations for every seizure recorded in each cKO animal in the study. C, Representative EEG traces from the left and right recording electrodes in cKO mice showing the two main types of seizure activity based on electrographic pattern. Type 1 seizures were generally associated with mild, non-convulsive behaviors, whereas type 2 seizures were associated with more severe, tonic-clonic behaviors. D, Total number of seizures segregated by type for each seizure-positive cKO mouse. Seizures classified as “other” exhibited a mixture of EEG patterns that could not be categorized as solely type 1 or 2. E, Quantification of the time latency to generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTCS) upon exposure to flurothyl in WT (n=5), Cre (n=6), fl/− (n=5), and cKO mice (n=4). *P=0.04; ##P=0.006 (1-way ANOVA; post-hoc Tukey test).