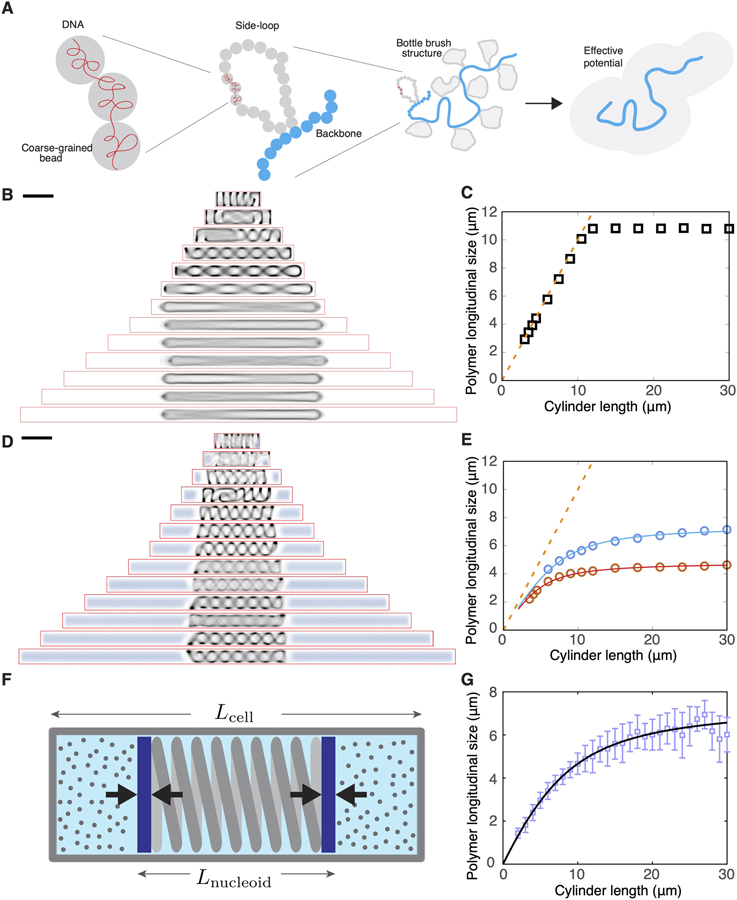
Figure 3. A Polymer Model Captures the Effect of Boundary Confinement on Nucleoid Size and Position.
(A) Schematic of the construction of our coarse-grained polymer model of bottle-brush type, with a bead-chain circular backbone and side loops represented by a parametrized effective potential.
(B) Time-averaged conformations of our model chromosome simulated in cylindrical cells of different lengths in the absence of depletants.
(C) Longitudinal size (FWHM of the backbone) of the modeled chromosome polymer as a function of cell size, simulated without depletants. The orange dashed line indicates the cell length.
(D) Time-averaged conformations of our model chromosome simulated in cylindrical cells of different lengths in the presence of depletants at density of 212 μm3.
(E) Longitudinal size (FWHM of the backbone) of the modeled chromosome polymer as a function of cell size, simulated with two different concentrations of depletants. Blue circles indicate a depletant density of 212 μm−3, and red circles indicate a depletant density of 1,060 μm−3. The orange dashed line indicates the cell length. The two solid lines represent fits to the piston model, Equation 1.
(F) Schematic describing the piston model.
(G) Fit of the piston model (green line) to the experimental data.
Scale bars in (B) and (D), 2 μm. See also Figure S4.