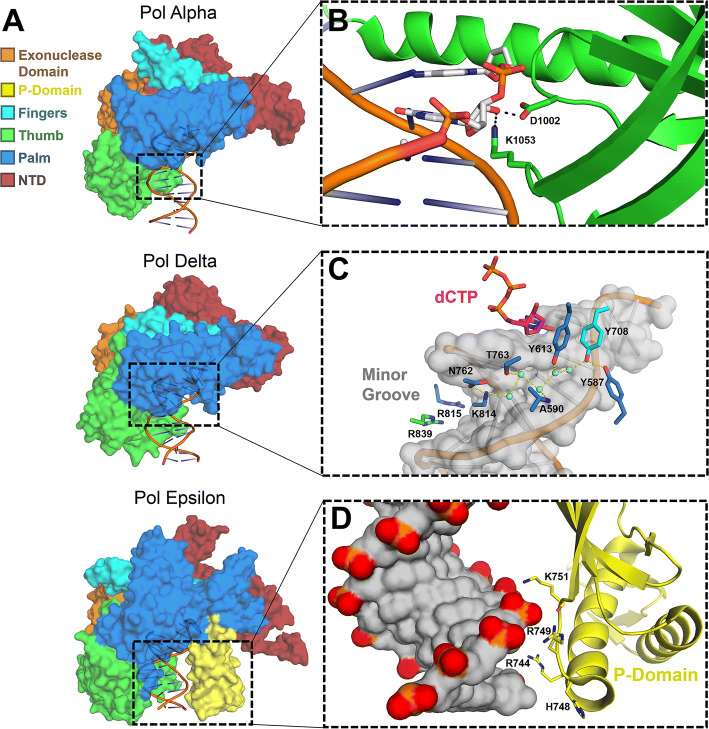
Fig. 1.
Overall structure and specific features of replicative B-family polymerases. a Surface representations of human pol α (5IUD), yeast pol δ (3IAY) and yeast pol ɛ (4M8O) are shown with their exonuclease (orange), P-domain (yellow), fingers (cyan), thumb (green), palm (blue), and N-terminal (red) domains highlighted. b A close-up view of the pol α thumb domain (green) making contact with the 2′-OH groups of the RNA of its DNA/RNA hybrid substrate (white sticks), the product of its primase activity (4Q5V). c The minor groove of nascent DNA probed by Pol δ through direct contacts (blue sticks), as well as through coordinated water-bridges (cyan spheres; 3IAY). d The P-domain (yellow), found only in Pol ɛ, provides additional contact to the nascent DNA (gray surface; 4M8O)