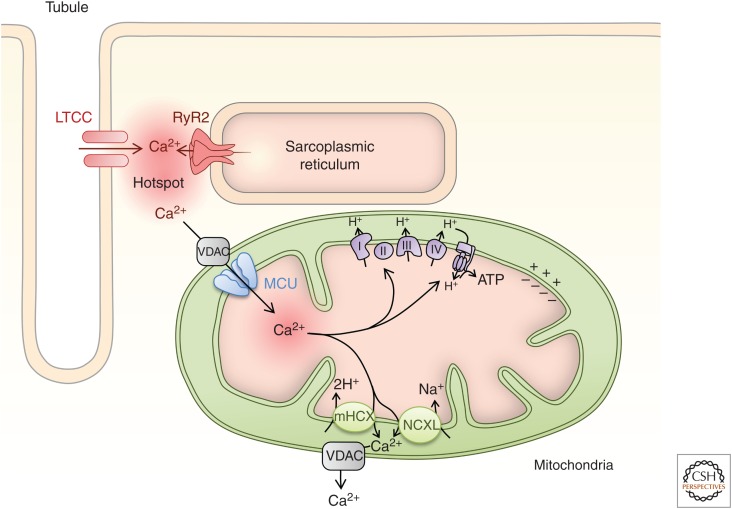
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial Ca2+. Mitochondria are densely packed in the cardiomyocyte being aligned along the myofilaments as bricks. Their Ca2+ uptake sites are closely localized to the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and a microdomain of elevated Ca2+ generated by SR Ca2+ release via RyRs. Ca2+ enters the mitochondria through the voltage-gated anion channel (VDAC) of the outer mitochondrial membrane and the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU) of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Ca2+ acts at multiple sites in the electron transport chain and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to modulate mitochondrial metabolism and ATP production. Ca2+ is extruded from the mitochondria through a Na+/Li+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCXL) and/or a Ca2+/H+ exchanger (mHCX).