FIGURE 1.
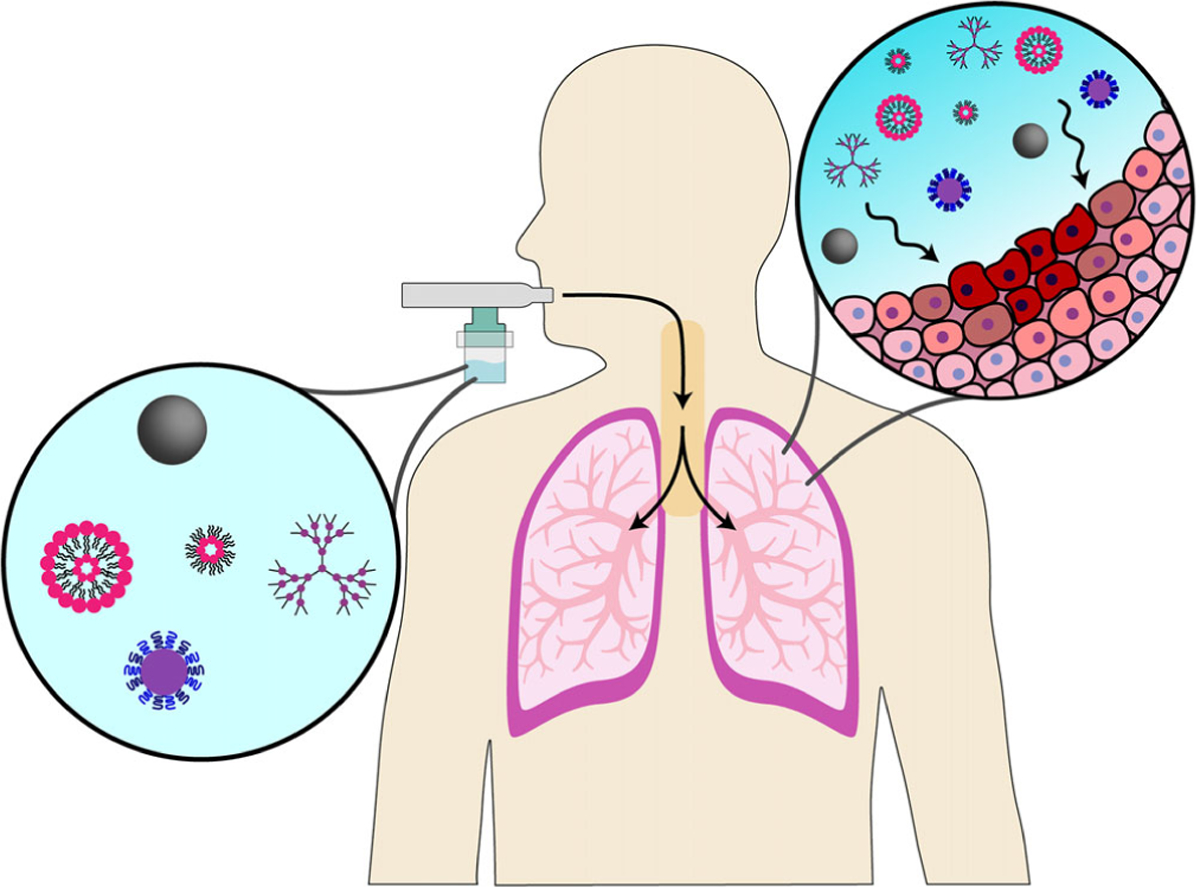
A wide variety of nanomaterial systems have been employed to develop inhalable nanomedicine systems (depicted here are liposomes, micelles, polymeric nanoparticles, dendrimers, and magnetic nanoparticles as examples of designs explored for this application). After administration with various aerosolization devices (jet nebulizer represented here), these systems are noninvasively delivered directly to lung tissues to passively target diseased cells. For a variety of respiratory diseases, this is advantageous as it enhances therapeutic efficacy and mitigates systemic toxicity, which can be further improved by decorating nanomaterials with targeting moieties for a particular lung disease
