FIGURE 7.
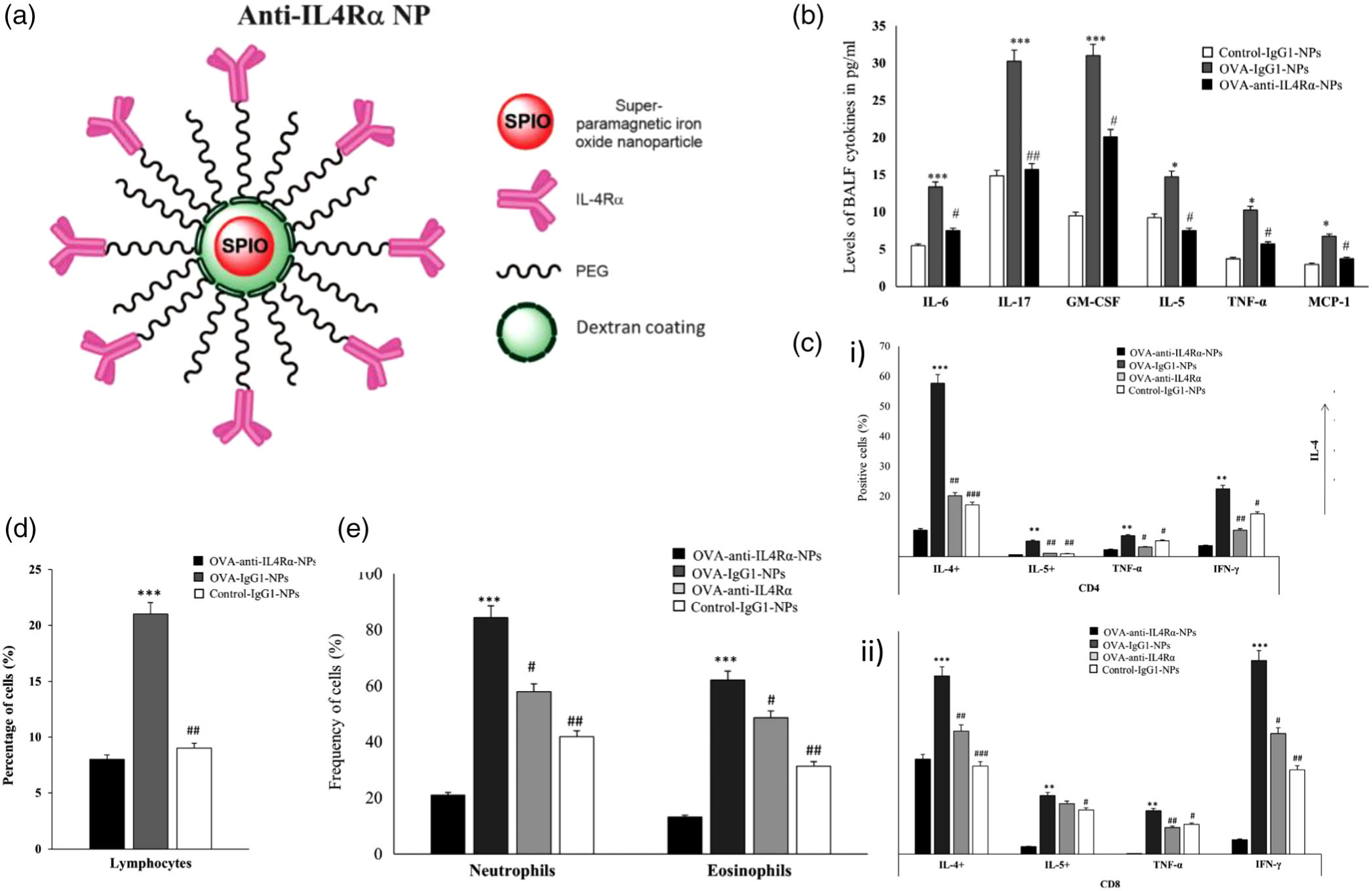
Design, inflammatory cell response, cytokine release, and immunohistological imaging of an anti-IL4Rα-NP system. (a) An illustration representing the design of the anti-IL4Rα NPs. (b) BALF levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice treated with or without the anti-IL4Rα-NPs, where cytokine levels decreased in mice treated with anti-IL4Rα-NPs. (c) i) CD4 and ii) CD8 T cells isolated from the lungs of ovalbumin (OVA)-challenged mice treated with or without the anti-IL4Rα-NPs, highlighting attenuated inflammatory marker expression from anti-IL4Rα-NP treatment. (d) Effect of the anti-IL4Rα-NPs on the BALF inflammatory cells in the treated OVA-challenged mice showing observed decrease in lymphocyte frequency. (e) frequencies of neutrophils and eosinophils isolated from the lungs of OVA-challenged mice treated with or without anti-IL4Rα-NPs, showing decreased levels of both cell types from the anti-interleukin-4 receptor α (IL4Rα)-NPs (for control vs OVA: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; for OVA vs anti-IL4α-NPs: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01). (Reprinted with permission from Halwani et al. (2016). Copyright 2016 Springer Nature)
