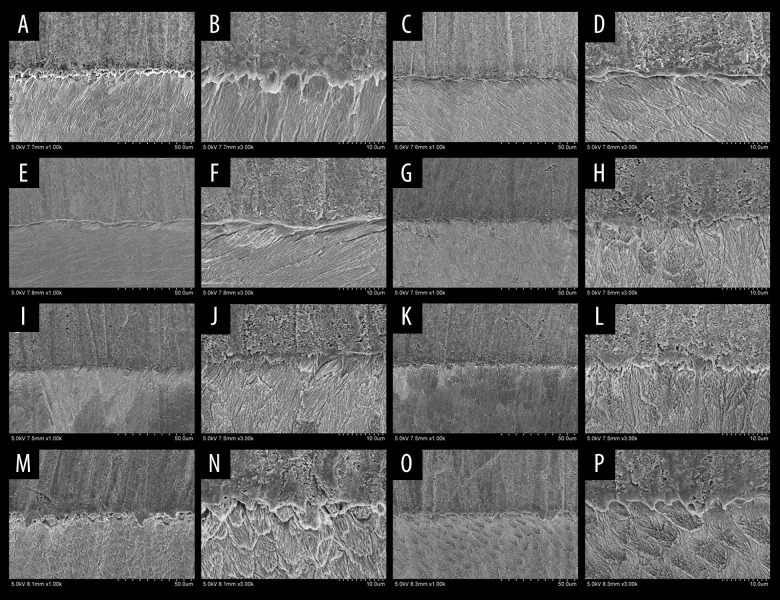
Figure 4.
Scanning electron microscopy pictures after bonding tests of all groups. (A, B) The negative control (NC) group showed that the resin-enamel interface was compact, without crack, along with the closely chimeric resin process and enamel. (C, D) The no antioxidant (NA) group demonstrated that the interface between enamel and resin cement was loose and cracked. (E, F) The sodium ascorbate at 30 minutes (SA30) showed that the interface of group 3 was denser than group 2, but there were still cracks. (G, H) The sodium ascorbate at 60 minutes (SA60) group and (I, J) the sodium ascorbate at 120 minutes (SA120) illustrated that the interface between enamel and resin was compact and crack-free, along with chimeric the resin process and enamel. (K, L) The proanthocyanidins at 30 minutes (PC30), and (M, N) the proanthocyanidins at 60 minutes (PC60) showed that the interface between enamel and resin was clear, but the band was loose. There were scattered cracks resin protrusions. (O, P) The proanthocyanidins at 120 minutes (PC120) showed that the interface between enamel and resin cement was not clear, along with the solid bond, without crack. The formation of resin protrusion could be observed.